Pregnancy And Hormones
Contents:
- Why is it Necessary to Control the Level of Hormones?
- Hormones that “Produce” the Body of the Future Baby
- The Pregnancy Hormones
- Thyroid Hormones
- The Motherhood Hormones
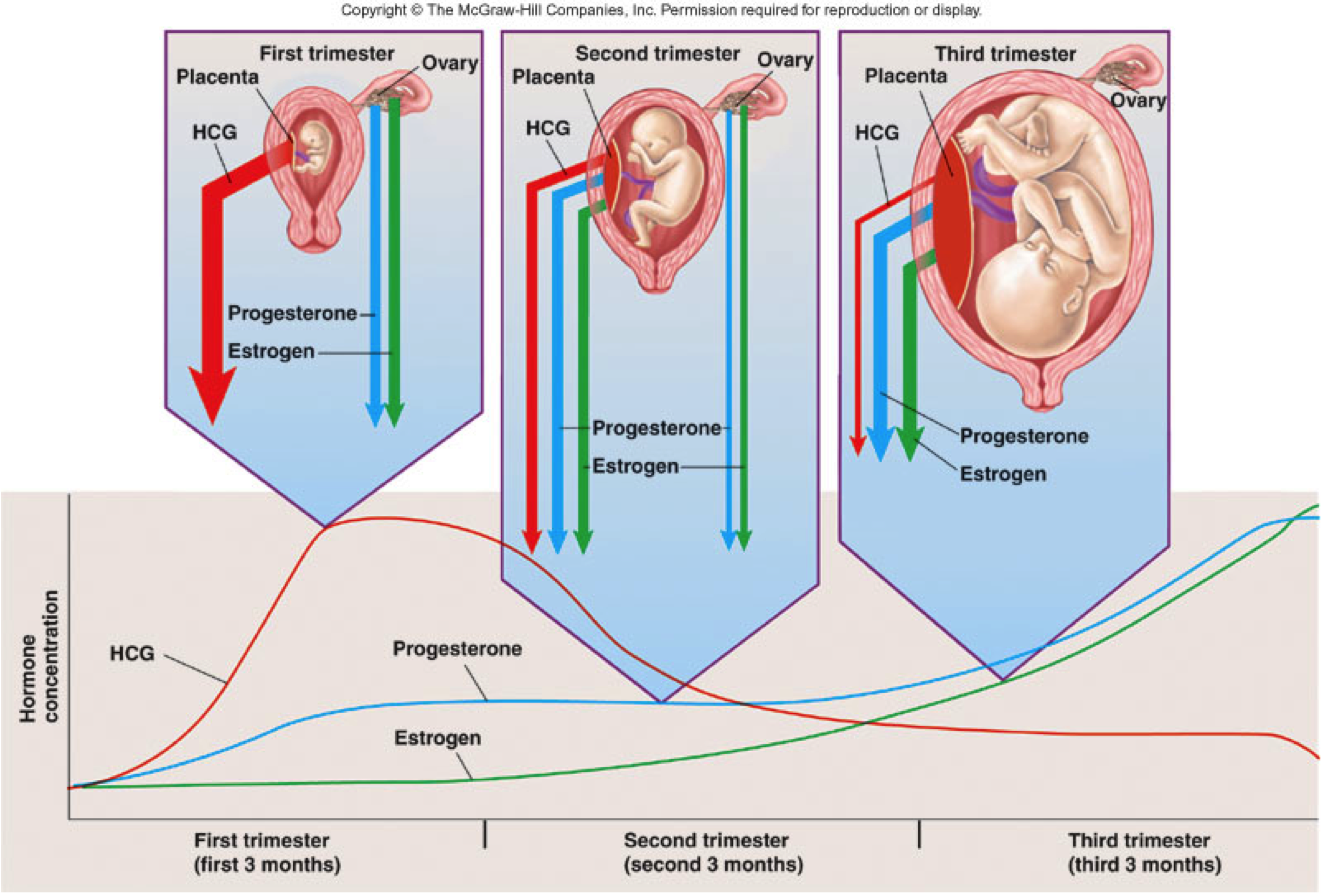
Hormone Levels During Pregnancy
Hormones are amazing biologically active substances, which affect not only health but also human’s mental world. Nature provides activation of special pregnancy hormones in woman's body that starts immediately after the conception. These hormones not only help the baby to develop completely but also set up a future mother for her wanted motherhood, teach her to love her baby growing inside and let her get used to take care of him.
Why is it Necessary to Control the Level of Hormones?
While waiting for the childbirth, the whole woman’s body faces with serious changes – especially in the hormonal levels. The changes occur in the entire endocrine system. The body of the future mother, being completely reconstructed, creates conditions for the normal development of the pregnancy and the baby, and starting from the first days of pregnancy it begins to prepare for the delivery.
All hormonal indicators of the future mother’s body play a huge role, specifically, they are the most important indicators of fetal development. Therefore, the level of hormones is being obligatory controlled by the attending physician with the help of special surveys – prenatal screenings that a woman during pregnancy needs to have at least 2 times: in the first trimester (11th-12th weeks) and in the second trimester (16th-19th weeks). Let’s see, which medical parameters are included in this obligatory test, what the increase or decrease in the level of a hormone means, and what roles the hormones have.
Hormones that “Produce” the Body of the Future Baby
HCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin). This hormone is actively produced by cells of chorion (birth membranes) immediately after it is attached to the uterine wall. This hormone production is essential for the preservation and maintenance of pregnancy. HCG controls the production of the main pregnancy hormone – estrogen and progesterone. With a serious lack of HCG fertilized egg detaches from the uterus, and menstruation occurs again – in other words, a spontaneous miscarriage occurs. Normally, the concentration of HCG in the expectant mother’s blood is constantly increasing, reaching a maximum in 10th-11th weeks of pregnancy, and then the concentration of HCG gradually decreases to remain unchanged for up to the delivery. The HCG test during pregnancy is very important.
First, the blood test for HCG level is able to confirm that you will become a mother already on 5th-6th day after the conception. This test shows the correct result much earlier and, more importantly, much more reliable than the conventional strip tests. Secondly, you need to have this test to determine the exact term of pregnancy. Very often the expectant mother cannot give the exact date of conception or says it in a wrong way. However, each term is characterized by specific indicators of growth and development, the abnormalities in which may indicate the occurrence of complications. Third, the HCG level in the blood is able to “tell” completely whether your baby is developing right.
Unplanned increasing of HCG level usually occurs in case of multifetal pregnancy, gestosis, synthetic progestogens intake, diabetes, and it may also indicate some hereditary diseases of the baby (such as Down's syndrome) and multiple malformations. Abnormally low levels of HCG may be a sign of ectopic pregnancy and non-developing of fetus, delays in fetal development, miscarriage threat, chronic placental insufficiency.
But however you need not worry too much: higher or lower HCG levels may also say that the gestational age was originally determined incorrectly. Your doctor may help you to interpret the test results right. Placental lactogen and theelol. Controlling the level of these hormones is very important to assess the risk of hereditary chromosomal abnormalities in the unborn baby (this is Down syndrome, Edwards, Turner, Patau, neural tube defects, and so on).
Theelol is “produced” by the placenta. This hormone improves blood flow through the uterine vessels, as well as contributes to the development of the mammary glands ductules, preparing the organism of the future mother for feeding the baby.
The level of theelol changes under any pathological conditions:
- in case of placental insufficiency when the normal blood flow and placental nutrition change;
- in case of fetal growth retardation;
- at suspicion on a prolonged pregnancy.
Placental lactogen (PL) is also “produced” by the placenta, and it can be found in the future mother's blood starting from the 5th-6th weeks of pregnancy. It reaches the maximum value on 37th-38th week of pregnancy, and then its level gradually decreases. However, the PL level must be tracked during the whole pregnancy – first of all, it is necessary for assessing the state of the placenta and diagnosing the placental insufficiency in time. The sharp decline in the PL level more than in 2 times (compared to the average PL level for the exact pregnancy term) can indicate the delay in fetal development. In this case, it is necessary to assume urgent measures to prevent the PL level reduction at 80 percent or more – it can cause the death of the baby.
The Pregnancy Hormones

Estradiol and progesterone. The pregnancy hormonal tests necessarily include an analysis of the progesterone and estradiol levels. These hormones take care of your future baby, maintaining the normal course of pregnancy, and therefore they are called the principal gestation (pregnancy) hormones.
Estradiol is normally produced by the ovaries, and during pregnancy it is also produced by placenta. During pregnancy, the level of this hormone increases dramatically, and no wonder – estradiol is “responsible” for the normal course of pregnancy. In the early stages, through the concentration of this hormone the functioning of the placenta is assessed. Reduced estradiol level indicates a serious threat of pregnancy termination.
By the way, under the influence of this hormone a woman experiences a natural desire to “make a nest”, to equip and prepare everything for the childbirth. Before the delivery, the concentration of this hormone in the body of the expectant mother reaches its “peak”, which is also explained by natural causes – estradiol is a strong natural analgesic, helping to make the process of childbirth less painful.
Progesterone is also the main “pregnancy hormone”; its main task is to preserve the pregnancy and to create the necessary conditions for the development of the fetus. Normal progesterone level is necessary for the conception itself. Together with the estrogen, this hormone provides the attachment of the fertilized ovum to the endometrium and “carefully” mitigates the increased tone of the uterus, preventing the miscarriage. During the gestation, progesterone stimulates the growth and maturation of the mammary glands, preparing the body of the expectant mother to breastfeed, both psychologically and mentally, as it calms down and supports her. Unfortunately, this hormone also has “side effects” that are familiar to every pregnant woman – it causes drowsiness, nausea, frequent urination, pain and swelling of the breasts.
With a lack of progesterone, the serious complications may occur during the pregnancy. The deficiency of this hormone needs to be urgently refilled, otherwise the risk of non-developing pregnancy and miscarriage increases. IMPORTANT! Estradiol and progesterone levels test is carried out both during pregnancy and in preparation for the delivery, it is particularly necessary in cases if a woman already has had miscarriage.
Thyroid Hormones
A major role for the development of the baby belongs to a normal functioning of the expectant mothers thyroid gland. The presence of hypo- or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland can be also indicated by the appropriate hormones (TSH, T3 and T4).
The Motherhood Hormones
The critical role for gestation also belongs to pituitary hormones (endocrine gland, located in the hypothalamic brain region). During delivery, the pituitary gland releases the oxytocin hormone into the bloodstream; it stimulates uterine contractions. And after the delivery the active synthesis of the prolactin hormone begins, it is “responsible” for the lactation. With a lack of prolactin the woman simply cannot normally feed her baby with breast milk.
Furthermore, prolactin and oxytocin are also called “motherhood hormones” because thanks to them, mothers heart is filled with tenderness, she feels the pleasure of feeding and communicating with the child, which makes her even closer to the baby. These hormones, in fact, provide a magical “transformation” of woman into the mother – under their influence her priorities change dramatically, her education, work, career and personal success fade into the background, and the main place in her heart now belongs to a dear little creature.
It is believed that the more a woman has these “motherhood hormones”, the more is her desire to be near the baby constantly, to feel its warmth, to take care of it. But do not expect this “transformation” to happen as if by magic: normally, the levels of these hormones in a woman's body change gradually, so that her mind would prepare for the changes taking place with no stress.