The Test Of Tolerance To Glucose During Pregnancy
Contents:
- Why a Glucose Tolerance Test is Performed?
- Stages of Diagnosis Disorders in Pregnancy
- Is there a Special Preparation
- How is OGTT Conducted
- What Blood Sugar Levels Indicate GD
- Is there Any Danger Associated With the Test?
Why a Glucose Tolerance Test is Performed?
An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is a testing for glucose tolerance. It helps to identify the disorders of carbohydrate metabolism during the pregnancy and find out how woman's body regulates the sugar levels. This test can detect gestational diabetes (GD) – the increase of blood sugar levels associated with pregnancy.
GD may be identified in women without previously diagnosed diabetes, because pregnancy itself is quite a significant risk factor for disorders of carbohydrate metabolism.
Gestational diabetes usually has no pronounced symptoms. That’s why this test must be done in time in order to start treatment as soon as possible, as GD may have negative consequences for both mother and baby. In the period between 24-28 weeks (preferably between 24-26 weeks), all pregnant women should undergo an OGTT involving 75 g of glucose.
Stages of Diagnosis Disorders in Pregnancy
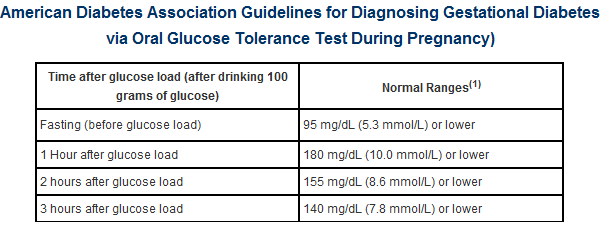
Stage 1. Before the 24th week of pregnancy the fasting blood test is performed, the first conclusions are made upon the results:
- normal result is below 5.1 mmol/l (92 mg/dl);
- if the result is above 5.1 mmol/l (92 mg/dl), but below 7.0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) – the diagnosis is GD;
- if the result is above 7.0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) – the provisional diagnosis is new onset diabetes mellitus (SD).
Some doctors offer women that enter the gestational diabetes risk group undergo 75 g glucose OGTT immediately after the registration. If the result is negative, a retest is to be performed between 24-28 weeks.
Stage 2. Women who had no symptoms in the early stages undergo the glucose tolerance test between 24-28 weeks.
Is there a Special Preparation
To undergo an OGTT you will be required to have at least 150 g of carbohydrates per day for three days prior to the test. GD is impossible to identify if a woman keeps to a special diet.
The OGTT is usually scheduled in the morning, as you will be prohibited to eat anything for at least 8-14 hours. However, you will be allowed to drink water. At least 24 hours prior to the test it is forbidden to consume alcohol. You cannot smoke until the end of the test. You should try not to take any medications that could affect your blood sugar levels (adrenoceptor blocking drugs, glucocorticoids, multivitamins, iron supplements containing carbohydrates, etc.).
The glucose tolerance test can’t be performed in cases of:
- early pregnancy toxemia (vomiting, nausea);
- dumping syndrome or aggravation of chronic pancreatitis;
- acute inflammatory or infectious diseases;
- you have to keep to a strict bed confinement (you can test after an increase in the number of movements).
How is OGTT Conducted
The test is conducted in a sitting position. Any physical exercise (even walking) can affect the result. The blood is drawn from a vein. You cannot use your glucometer.
Stage 1. A vein blood sample is drawn. Glucose levels are measured. If the result is above the normal (5.1 mmol/l), the test is interrupted and gestational diabetes or overt diabetes is diagnosed. If it is impossible to measure the glucose levels, the test is conducted till the end.
Stage 2. The pregnant woman should drink a glucose solution within five minutes after the blood sampling (250-300 ml of water with 75 g of anhydrous glucose or 82.5 g of glucose monohydrate). The moment when the woman begins to drink the glucose solution is considered to be the beginning of the test. The glucose solution is a lusciously sweet drink. Some women experience nausea and vomiting drinking it. No need to drink this solution in one gulp. It is recommended to add a few drops of lemon juice to give it a certain freshness of taste.
Stage 3. Within 1-2 hours after you drank the glucose solution the blood is drawn again (the next sample is to be collected in 2-hour interval). If the blood sample collected within an hour proves the diagnosis of GD, the test is interrupted. In some cases, 75 g OGTT is conducted up to the 32th week.
What Blood Sugar Levels Indicate GD
The borderline level of venous blood glucose that diagnoses for gestational diabetes: (recently the threshold was raised as it was proved that elevated levels of glucose in blood affect the fetal development).
It’s enough to have one abnormal reading of three for a diagnostic of GD. So if the first fasting sample glucose is above 5.1 – the second stage is cancelled, and if the second one-hour sample is above 10.0 – the test stops and the diagnosis of gestational diabetes is established.
Quite often clinics practice "trial with breakfast”: the blood is drawn (as a rule it’s a fingertip blood sample), then the woman eats something sweet and after some time again the blood is collected. Such a test cannot use conventional borderlines, as the breakfast varies on the person and the result may be inaccurate.
Is there Any Danger Associated With the Test?
75 g of anhydrous glucose dissolved in water is equal to a breakfast that consists of a sweet pie. In other words, OGTT is safe. It cannot cause diabetes. On the contrary, if a woman refuses to undergo the glucose tolerance test, and the gestational diabetes is unidentified and no necessary measures are taken, it may cause serious problems for both mother and baby.