Sty In Babies
Contents:
- Sty in Children
- Causes of Sty in Children
- Symptoms of Sty in Babies
- Diagnosing Sty in Children
- Treatment of Sty in Children
- Prevention Sty in Children and Prognosis
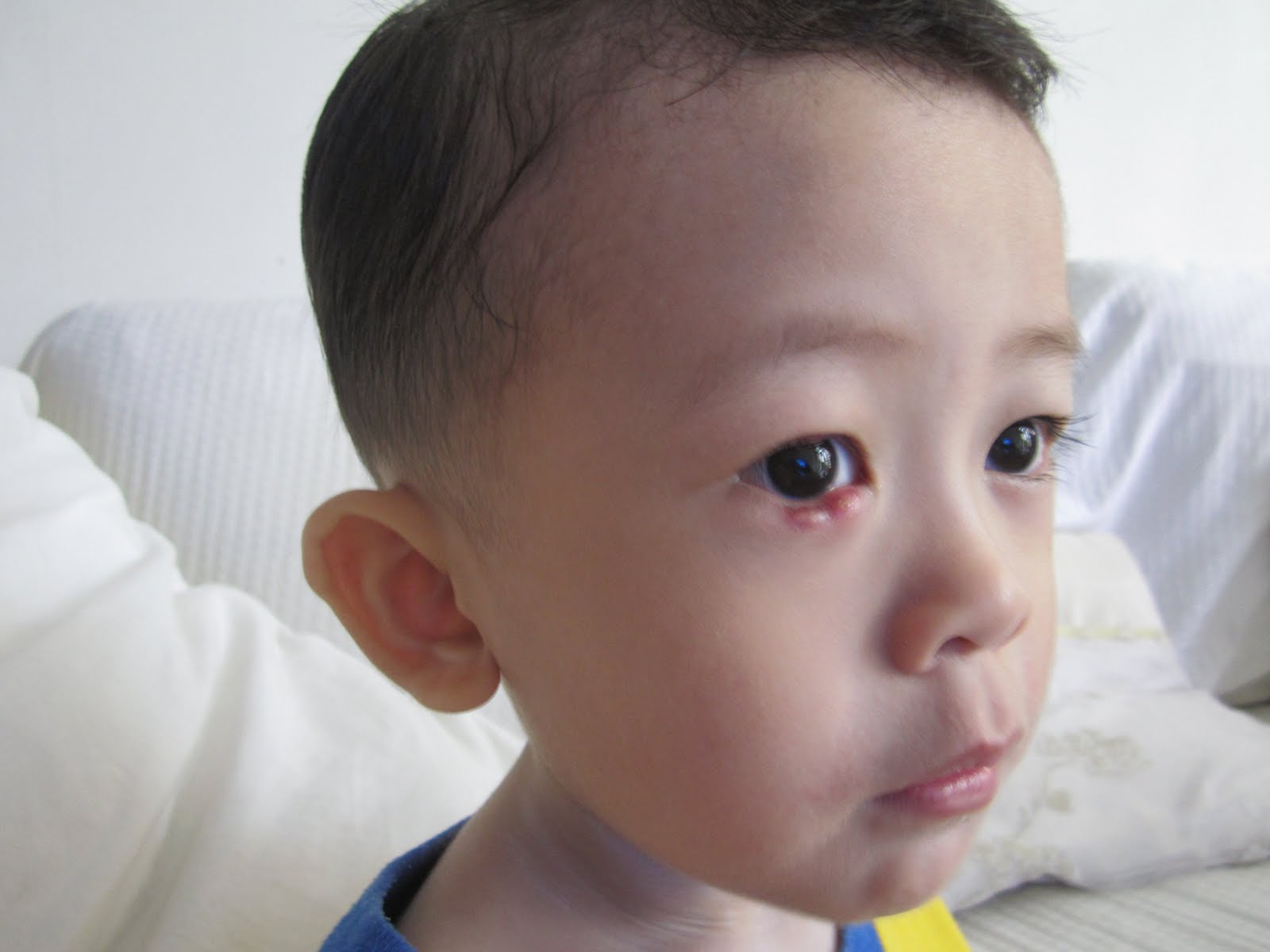
Stye in Baby Eye
Stye in case of children is a limited accumulation of pus in a hair follicle of an eyelash and connected with it Zeis sebaceous glands. It’s more rarely when this accumulation occurs in lobules of meibomian glands that are located in the thick of palpebral cartilages.
The clinical picture of the disease in case of a child is characterized by a painful swelling and hyperemia of an eyelid, the formation of abscess at the root of an eyelid (external sty) or at the inner side of an eyelid (internal stye). Later on, the abscess rips up and pus goes out. The disease in case of children is diagnosed on the base of general examination of eyes and eyelids when there is natural and side light.
In case of children’s sty clearing out, disinfection of the infiltrate, use of eye drops and ointments with antibacterial effect are recommended. If there is a need, the abscess is to be ripen up surgically.
Sty in Children
Sty in case of children is an acute local pyoinflammatory process that affects hair follicle of an eyelid and Zeis sebaceous glands. Sometimes, the disease affects big meibomian glands of tarsal- conjunctival plate. Stye in case of children very often occurs in clinical practice of pediatrics and children’s ophthalmology.
There are the following types of sty: an inner and outer sty, single and multiple sty, one and two-sided sty in case of children. An outer sty occurs more often. It is characterized by a suppurative focus on the edge of an outer skin-muscle plate of an eyelid at the root area of eyelashes. In case of an inner sty (meibomitis) a child has a pus inflammation in the thick of a cartilage plate of an upper or lower eyelid. The abscess then moves on to the inner mucous area that adjoins a globe of the eye.
Once sty is formed it looks like an accumulation of polymorpho-nuclear leukocytes and necrosis of tissues. In other words, it’s an abscess.
Causes of Sty in Children
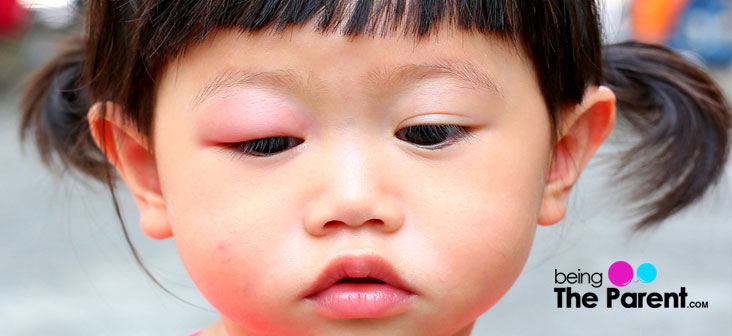
Sty in case of a child is an acute local infectious process that’s caused by bacterial microflora. Actually, in 90-95 % of cases it’s caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The infection (that’s then is followed by the development of sty) gets into the area of a hair follicle and ducts of the sebaceous glands. This situation occurs if a child doesn’t follow the rules of personal hygiene, touches and scratches the eyelids with dirty hands, uses dirty towel and also in case a child wears contact lenses or swims in a dirty pond.
When infection gets into the ducts of sebaceous glands, their excretory channels get stoppered and the stasis of secretion occurs. All these things make the inflammation only worse. The immune system being not developed enough and weak protective mechanisms of an organism (caused by very often cases of ARVI, chronic focuses of such infections (tonsillitis, adenoiditis, sinusitis), diseases of gastrointestinal tract, parasites invasions (ascaridiasis, toxoplasmosis), endocrinopathy (hypotheriosis, diabetes) and avitaminosis) contribute to the development of pyoinflammatory processes on the skin of a child.
The case of a child’s stye is often accompanied by other damage of eyes (staphylococcal blepharitis, conjunctivitis, dysfunction of meibomian glands). While a child is in his or her teens, the disease makes the course of seborrheic dermatitis, acne vulgaris, furunculosis and demodicosis. If there is a case of HIV, chronic course of sty and other bacterial infections of skin occur.
Symptoms of Sty in Babies
Clinical picture of sty in case of children is characterized by an acute start and symptoms that start occurring very fast. The formation of outer sty starts with the appearance of hyperemia and swelling on a limited area of an eyelid, on the site where eyelashes grow. A child starts complaining about painful sensations when he or she blinks or when he or she touches the place of the inflammation. There is also itching and prickling. The eyelid swells and gets thicker. This leads to the narrowing of palpebral fissure, sometimes it leads to the situation when it’s impossible to open the eye.
Inflammatory infiltrate gets bigger in size very fast. On the 2nd or 3rd day of the disease, as a result of suppurative inflammation, there is a formed abscess that has a yellowish head at the root of the eyelashes.
After 1 or 2 days more, the sty rips up by itself and there is pus and pieces of skin necrosis. In case of children, the development of sty may go more rapidly since they have a habit to rub on their eyes. Once the sty is ripen up, the painful sensations get weaker as well as swelling and hyperemia of the eyelid. By the end of the week, all symptoms of the inflammation disappear.
In severe cases and in cases when there is multiple sty, a child may suffer from headache, high body temperature and general weakness that is accompanied by the increased size of the parotid and inframaxillary lymph nodes (lymphadenitis).
In case of an inner sty (meibomitis), the inflammation develops not so acutely, the swelling and hyperemia become more obvious if the eyelid is turned out. There may also be reddening and irritation of the eye’s conjunctiva. In case of an inner sty, a child’s abscess is ripen up from the inner surface of the eyelid and into a conjunctive sack.
After the inner sty ripens up by itself, there is a possibility of the eyelid’s mucous granulation overgrowth appearance. If the immune system of a child is weakened and there are focuses of chronic infection, the inflammation of the eyelids may become chronic in character with periodical recurrence of sty.
It’s forbidden to squeeze the contents of the child’s sty out since there is a danger of the purulent infection spread and the development of eye pit phlegmon, thrombophlebitis of the orbital eyelids and thrombosis of the brain’s canernous sinus. In rare cases, there is a possibility of purulent meningitis with a risk of death.
Sty in case of children may turn into chronic infectious lipogranulematoid inflammation of an eyelid’s sebaceous glands – chalazion.
Diagnosing Sty in Children
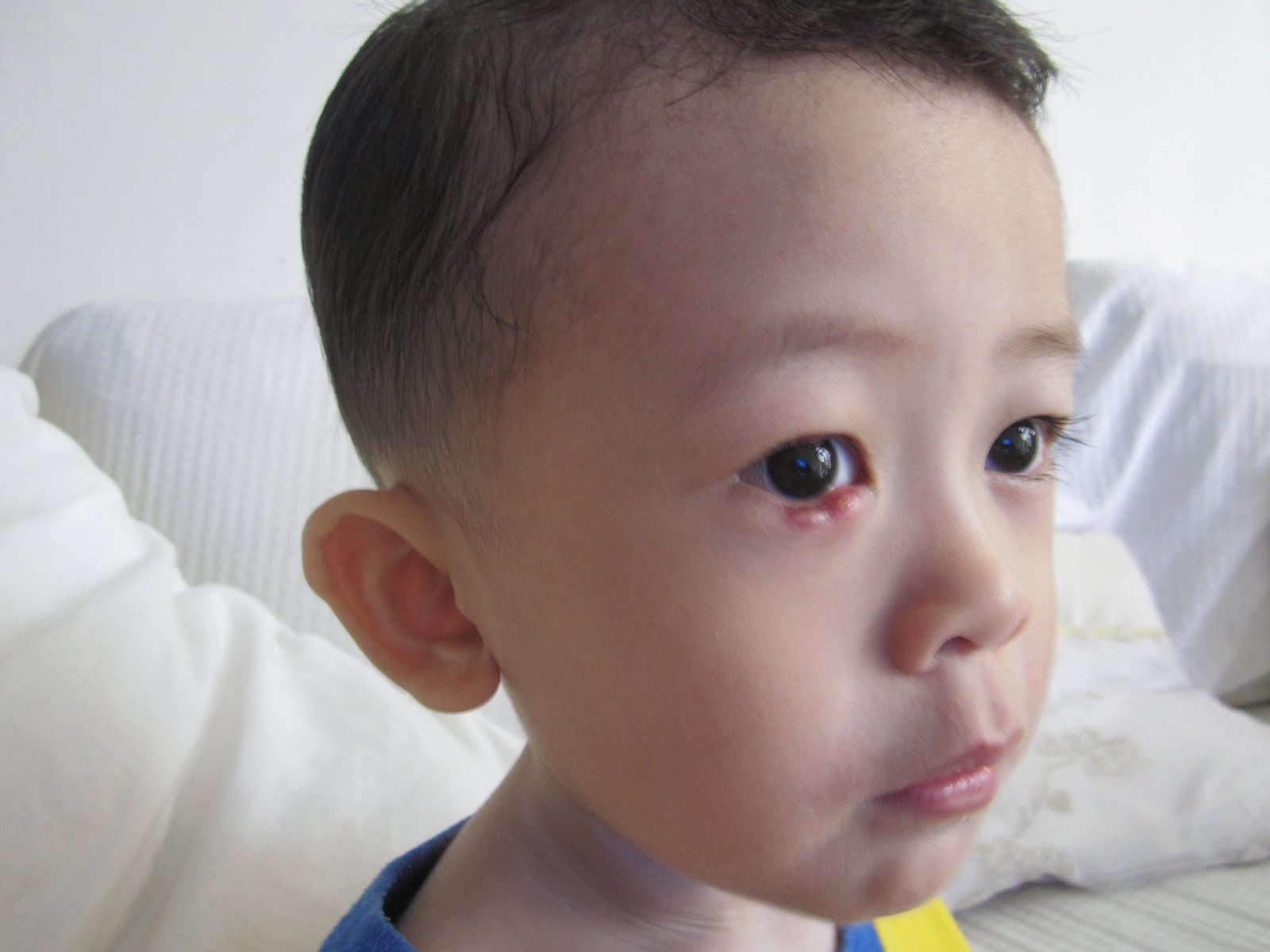
Sty is diagnosed in case of children be a children’s ophthalmologist on the basis of the eyes and eyelids general examination. The examination is carried out in the conditions of natural light and method of side light. Biomicroscopy of an eye in case of a child’s inner sty allows to detect a widening of meibomian gland’s canal.
In order to find out the reasons for the recurrence of sty in case of children an all-inclusive examination is carried out. There is also an opinion of a children’s immunologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist and endocrinologist taken into account. The patient is said to make a general blood and urine tests, the level of sugar in blood is found out. Also, bacteriological examination of swab from conjunctive (in order to detect the provocative agent and its sensitivity to antibiotics), a test of excrements on helminth eggs, an examination of eyelashes on demodicosis, an examination of immune status.
In case of children, sty is differentiated from chalazion, dacryocystitis, cysts and eyelids tumors.
Treatment of Sty in Children
Once you notice the first symptoms of sty, it’s necessary to immediately visit a children’s ophthalmologist. If the course of the disease is not complicated, the sty will be quite easy to cure and it will disappear in 7-10 days.
In the majority of cases, if there is sty, a local conservative therapy is carried out. At the beginning of the inflammatory process development, there is a clearing out and disinfection of the eyelids carried out every day. You are to treat them with chamomile decoction, flip the infiltrate over with 70 % ethyl alcohol and 1% decoction of brilliant green.
Before the head of the sty rips up, heat procedures that are to affect the focus of the inflammation are prescribed (blue light, UHF, warm heat). These procedures increase the inflow of blood and natural drainage. Eye drops are set into the conjunctive sack. These drops contain antiseptics (decoction of sulfacyl sodium), antibiotics (decoction of ciprofloxacin, levomycetin), glucocorticosteroids (decoction of dexamethasone).
Ointment pledges with Erytgromycyni and Tetracyclini Unguentum that are to be put under the eyelid are to continue even after the sty is ripen up. In order for the infection not to spread deeper when sty is being ripen up it’s necessary to keep an eye on your child and stop him or her from rubbing on the eyes.
In case general symptoms are developed (fever, malaise) it is recommended to take antipyretic, sulfanilamide and antibacterial drugs.
Surgical treatment is necessary in case of inner and outer sty of a big size that can’t be treated with conservative methods. The sty is ripen up under local anaesthesia that’s followed by an everyday post-operation treatment of the pus wound and antibacterial therapy. If there is a case of recurring course of sty, a child is prescribed to take vitamins, immune modulators and take a course of autohemotherapy.
Prevention Sty in Children and Prognosis
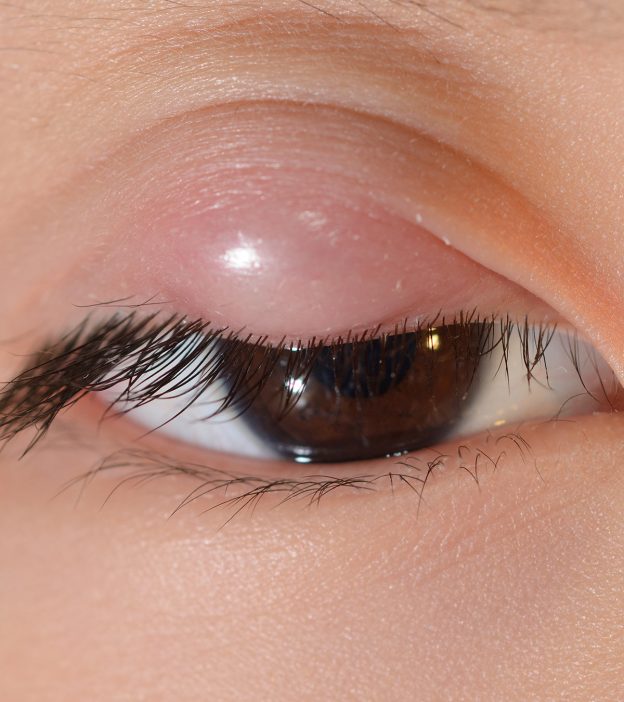
If the disease is treated adequately, as a rule, the prognosis is positive. In the majority of cases, there are no complications and the disease is cured within 1-2 weeks.
Preventive measures against sty in case of children include conditioning to cold, good eating, walking in fresh air, following the rules of personal hygiene, d-bridement of chronic focuses of infection. In case of sty recurrence, there is a need for a thorough examination with the aim to detect and eliminate etiological and predisposing factors.
Child Care and First Aid: How to Treat a Stye