Episiotomy During Childbirth
Contents:
- Why they Apply Episiotomy
- The Indications for Episiotomy
- How Operation Takes Place. Does it Hurt?
- How Rehabilitation After Episiotomy Should be Conducted
- Video: Episiotomy During Childbirth Delivery
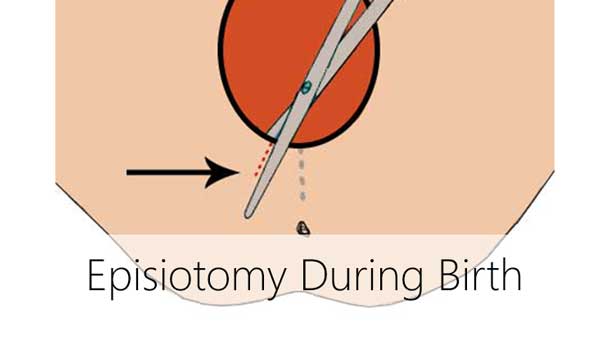
Childbirth Episiotomy
Episiotomy (a surgical incision of the perineum) is one of the most widespread surgical interventions during childbirth. Whether it is worth being afraid of it and whether it is possible to avoid it?
Why they Apply Episiotomy
Anyway, labor has just begun! Tissues of uterus cervix and perineum (it is a region of the body including a zone from the lower predetermined point of labia majora to the anus and also surrounding structures) stretch very strongly for the fetus could move along patrimonial ways. They should form the channel with diameter no less than 10 centimeters to let new-born baby get out into the light. At this stage a lot of things depend on the tissues elasticity: if they are well compliant, then tears or even a surgical incision can be avoided.
Some might believe that episiotomy is a way to facilitate a midwife’s job and to precipitate the child’s entering the world, or, simply put, "not to detain the doctor". This, however, is not the point of episiotomy. The procedure is intended to prevent a sizable rupture of the perineum which could have serious consequences up to loss of internal organs and rectum injury.
One important point is that the precise incision which is made by the surgeon during episiotomy heals with so-called "primary tension" and turns into a thin keloidal scar after sewing up. But in the case with the perineum rupture the situation is more difficult. The rupture means a wound with torn edges which heals with "a secondary tension", that is to say, uneven edges of a gap are filled with special developing granulation tissue which forms wound covering with big and amorphous keloidal scar.
The Indications for Episiotomy
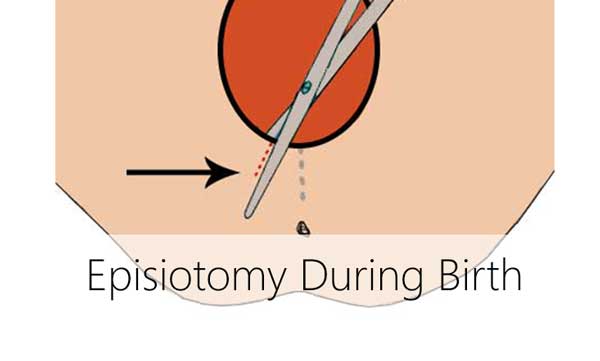
The need of the perineum incision can be defined only during delivery therefore such operation isn't planned in advance. However there may be situations when application of episiotomy can be predicted in advance. This operation is often applied in cases when childbirth has begun before its normal term. In such cases there is a risk of cerebral hemorrhage in an unripe brain of the prematurely born child due to high pressure of pelvic bottom muscles. So, the doctors have recourse to the surgical incision of the perineum taking care of the child.
The other widespread indication for episiotomy is a big fetus with the large head. In this case loading on even well extensible tissues could become overburden. One more often case when the perineum incision is applied is prompt childbirth. If the head of the child moves too quickly along patrimonial ways, then threat of serious vaginal tears also increases. This is because tissues just don't manage to stretch enough. Besides this, there may also be other indications.
How Operation Takes Place, Does it Hurt?
To decide whether there is a need for surgical interventions, the doctor supervises over a condition of tissues of uterus cervix and perineum when the fetus head has already moved forward enough along patrimonial ways and the child is ready to be born. If there is a threat of an expansion rupture, then the perineum tissues are modified. This becomes particularly prominent visually.
At first veins become pressed that causes stagnation of venous blood and therefore skin gets a bluish shade, then there is hypostasis and gloss of tissues, and at further pressing the arterial blood flow is impeded and skin turns pale. As a result, normal metabolic processes occurring in tissues are disordered. They become fragile and therefore threat of expansion rupture sharply increases. If the doctor has indicated such warning signs then he must recourse to the urgent episiotomy as to the only means.
As a rule, this operation can’t cause additional painful sensations – pain of the incision just isn't felt during labor bearing-down. But it isn't nice to feel sewing up cuts and tears, so therefore a local anesthesia is applied during this procedure most often, and in certain cases even the narcosis.
How Rehabilitation After Episiotomy Should be Conducted
Usually complete healing of scars occurs during about 4-5 weeks. During the first several days after the delivery sutures (as a rule, self-resolving sutures are imposed) are cleansed with antiseptic solutions.
To provide effective rehabilitation as fast as possible, the doctors recommend to follow several general rules:
- wash carefully your crotch each time after using a toilet;
- change sanitary napkins as often as possible;
- take air baths;
- walk more for blood circulation improvement;
- don’t allow constipation. Try a laxative at such problems with stool;
- if the pain is getting worse see the doctor urgently.
Of course, pain of sutures is not pleasant for young mother and rehabilitation after the delivery must not have been a comfortable period. However the most inconvenient (and often unexpected) episiotomy consequence is that it is impossible to sit at least a week after this operation (and some doctors forbid to sit down during even the whole month!) Feeding the child during this period is recommended lying or standing.
Skilled mummies advise: get a special anatomic rubber ring in a drugstore – it would reduce a tension of tissues and would give a real chance to sit. Some take seat also on children's inflatable rubber rings with success, but the main thing in that case is to select the ring size correctly. Above all ask your doctor whether you can sit on such circuit or not!