RH Incompatibility In Pregnancy
Contents:
- Causes
- What Happens In This Case
- Who Is Likely To Have The Rh Conflict
- Prevention
- Treatment RH Incompatibility in Pregnancy
RH Incompatibility During Pregnancy
Many of us have heard about Rh factor, but few people know what it actually is. That is not surprising, because Rh factor is a not something we deal with in everyday life. As soon as a couple start planning the pregnancy however, their incompatible Rh factors can form the Rh conflict.
Causes
Before we look into reasons that cause the Rh conflict, let’s find out what Rh factor is. Rh factor is an antigen (protein) on the surface of red blood cells (erythrocytes). It can be found in most of people (85%) and these people are Rh positive. The rest of the people (15%) do not have the Rh factor, which means that they are Rh negative.
There are two situations what can cause the Rh conflict. First is when an Rh-negative patient is given transfusions of Rh-positive blood. The other one happens when an Rh-negative mother has an Rh-positive fetus.
What Happens in this Case
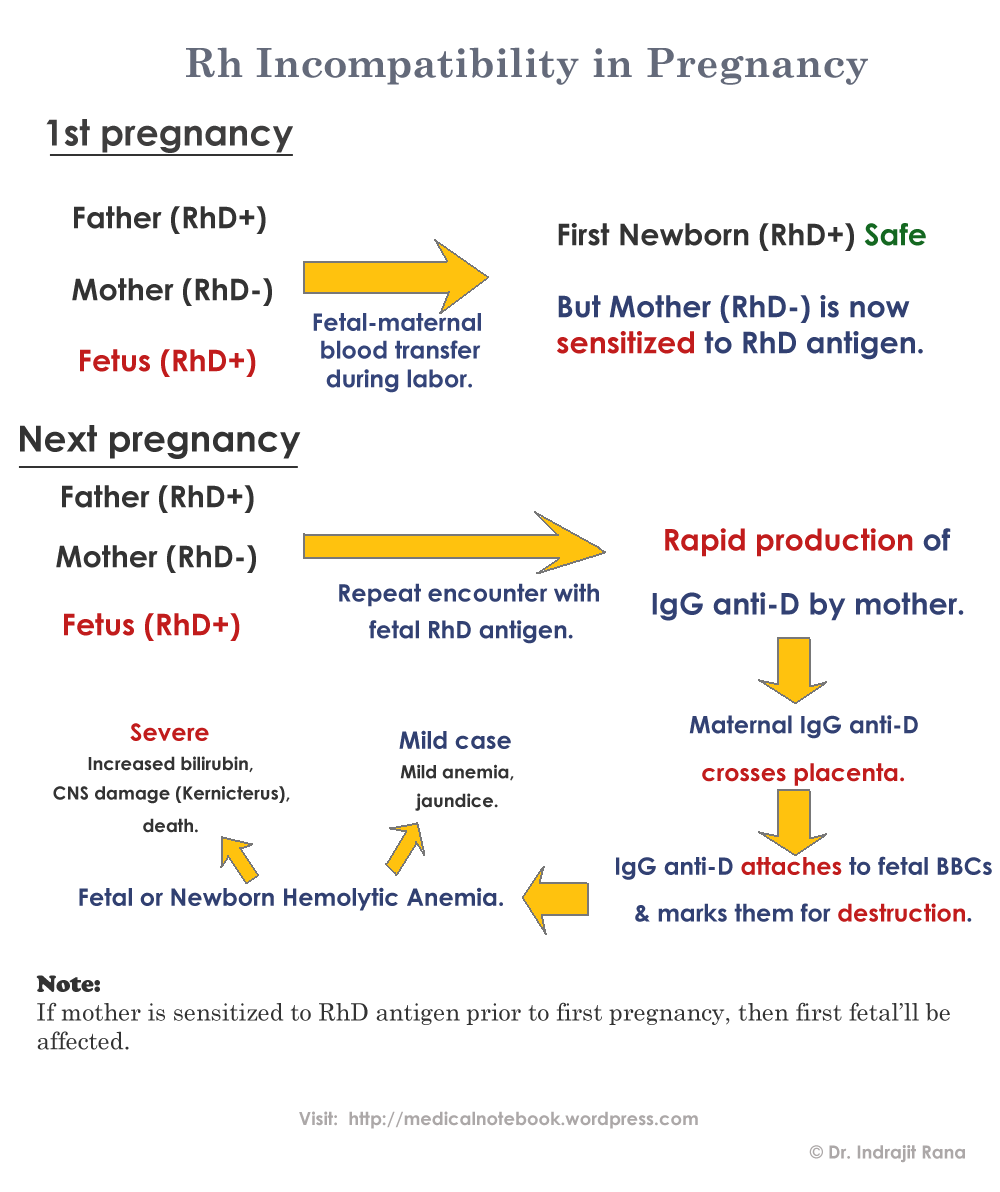
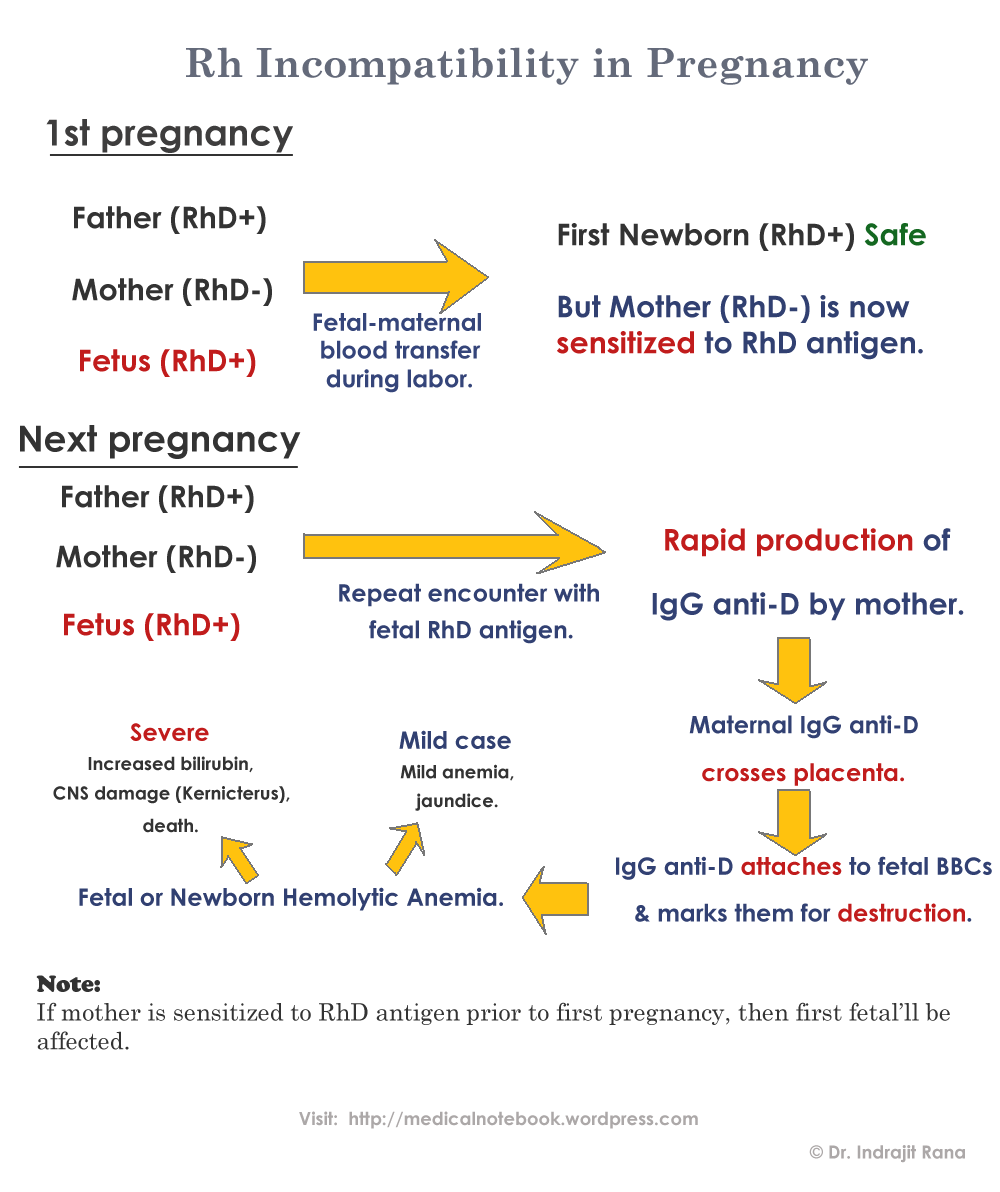
The Rh-negative mother’s immune system recognises the fetal erythrocytes with antigen proteins on the surface as foreign substances, and starts making antibodies against them. When erythrocytes are broken down they release haemoglobin that turns into bilirubin, a substance that in large amounts is toxic for the fetus and can damage its brain. The problem is caused when the liver and spleen work to restore the levels of erythrocytes, which causes them to enlarge in size. The shortage of haemoglobin causes oxygen deficiency that may lead to different complications in the fetus and even to death.
Who is Likely to Have the RH Conflict
Rh factor is controlled by genetics, as the antigen is inherited. The situation when an Rh-negative woman conceives a baby with an Rh-positive man, increases the chances of the Rh-conflict up to 75 %. This pregnancy needs special supervision by specialists, but it does not necessarily mean that it is impossible.
In most of the cases, Rh incompatibility is not a problem if it is the first pregnancy for the mother. Her blood, having no contact with Rh-positive blood, has no Rh-antibody titre yet. Hence, the Rh-incompatibility doesn’t develop during the first pregnancy. During the second pregnancy, the antibodies develop in such amounts that a positive outcome is likely to happen.
In cases where the erythrocytes of the fetus enter the mother’s circulatory system in large amounts, the mother’s body stores the so-called memory cells. During the future pregnancies, these cells will quickly attack the baby’s Rh factor with antibodies. The first pregnancy is very important for Rh incompatibility.
The following complications during the first pregnancy cause an Rh sensitization (antibodies production) to develop in future:
- Miscarriage – 3-4 %;
- Ectopic pregnancy – about 1 %;
- Therapeutic abortion – 5-6 cases;
- Natural childbirth – 10-15 cases.
The risk is higher with a placental abruption and C-section. Rh incompatibility is directly dependent on the amount of fetal erythrocytes entering the mother’s circulatory system.
Prevention
When a pregnant woman visits her doctor for the first time about her pregnancy, she has her blood tested for Rh factor. If the mother is Rh negative, then the father takes the blood test too. If the father is Rh positive, there is a potential for Rh incompatibility to develop. In this case, a set of measures is taken to prevent health problems and save the life of the baby. The future mom has to take blood tests every month until the 32nd week. These tests will show the production of antibodies and their amount compared to the amount of the baby’s erythrocytes. After the 32nd week, the blood test is taken every fortnight. A weekly blood test will be performed after the 35th week and up till the baby birth.
This thorough supervision helps to detect the possible start of Rh incompatibility and presence of Rh factor in the blood of the fetus. If the newborn is diagnosed with Rh factor, the mother is immediately (within 72 hours after the delivery) given Rh D immunoglobulin (serum). This measure helps to prevent Rh incompatibility in future pregnancies.
The same preventive measure should be taken in case of any complications during the pregnancy or surgical procedures with placenta, such as: abortion, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, mother’s injuries, chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis. The mother receives transfusions of Rh-positive blood with platelet concentrate along with Rh D immunoglobulin under the same conditions.
Treatment RH Incompatibility in Pregnancy
Rh compatibility can be confirmed if the blood tests show Rh antibodies presence and their number is growing. In this case, a woman is usually put into a prenatal care center where her pregnancy is constantly and closely monitored.