Urinary Tract Infection During Pregnancy
Contents:
- What Bacteria Cause Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women?
- What is the Danger of Infections of Urinary Tract in Pregnant Women?
- The Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women
- How Does Pyelonephritis Manifest Itself?
- Treatment of Acute Pyelonephritis
- Effects of Infections
What Bacteria Cause Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women?
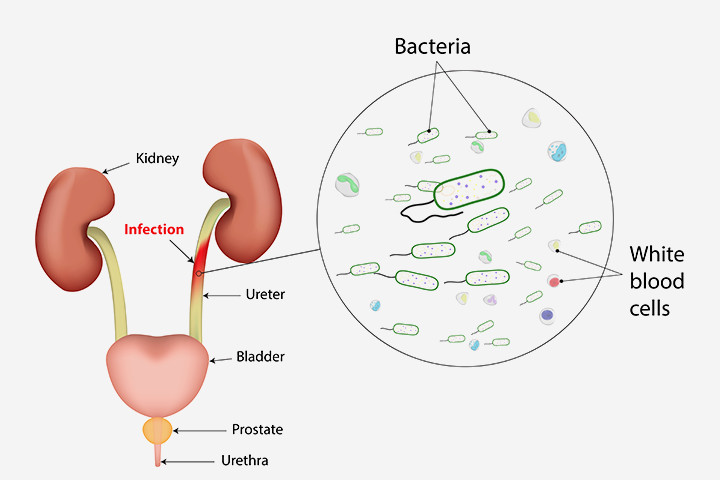
The main causative agent that causes the infection is escherichia coli. It is the cause of 80-90% of diseases. This infecting agent gets into urinary tract directly from the skin of the perineum. It appears on the skin due to anatomic proximity of the anus. Escherichia coli is a representative of normal microflora of the intestine of the person, but getting into unusual habitat conditions can cause inflammation. The composition of the remaining 10-20% of the bacteria, which can cause inflammation of the urinary tract during pregnancy include streptococcus, klebsiella, proteus, staph, various enterobacteria.
What is the Danger of Infections of Urinary Tract in Pregnant Women?
In most cases, the prognosis for all forms of infections is favorable. With complicated progress infectious-toxic shock, respiratory failure and limbs hypoxia, associated with low blood pressure may develop. The influence on the fetus is not strongly expressed, because the bacteria do not fall directly into the bloodstream of the fetus. However, such phenomena as dehydration of a mother, low blood pressure, anemia and direct effect of bacterial toxins can disrupt the blood supply to the brain of the fetus.
If urinary tract infection is not treated, there is the high risk of developing hypertension, preeclampsia, anemia, premature births, inflammation of the fetal membranes-amnionitis. Naturally, all these factors will significantly increase the risks of the unfavorable pregnancy and childbirth.
The Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women

With asymptomatic bacteriuria nothing bothers the pregnant. When the infection of lower urinary tract divisions develops, lower abdominal pain, frequent urination, hematuria appear. These symptoms are not strictly characteristic, as they may be caused even in healthy pregnant women due to compression of the bladder and pelvic organs by the growing uterus, increased urine formation and increase of volume of circulating fluid in pregnant women.
With pyelonephritis the body temperature rises (above 38 degrees), there is pain in the side, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. Sometimes, on the contrary, the body temperature may fall.
Diagnostics
If you experience symptoms that may be associated with the presence of urinary tract infection, a common blood test, urinalysis and analysis of urine by Nechiporenko method is done, as well as bacteriological test of urine (culture). These analysis also in routine procedure are carried out for pregnant women, who are on the file. In this way the monitoring for the presence of asymptomatic bacteriuria is performed. If there are suspicions of anomalies of urinary system or disruptions of its functions, an ultrasound of the kidneys is immediately carried out.
Also renal ultrasound is done when an antibiotic therapy does not improve during 49-72 hours. Despite the fact that specific ultrasound signs of cystitis and pyelonephritis do not exist, this checkup helps to identify structural changes in the urinary tract, such as the expansion of the ureter, pelvis, calixes, the presence of cystic-ureteric reflux. Also while doing kidney ultrasound ureteral obstruction by calculus is ruled out .
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women
Depending on the severity of the illness, treatment may be on an outpatient basis or in a hospital environment. Asymptomatic bacteriuria must obligatory be treated, as it is the main reason for the development of more severe diseases. Treatment can be divided into behavioral techniques and antibiotic therapy.
Behavioral methods include simple hygiene rules:
- You cannot take a bath during pregnancy, only a shower;
- Wiping the perineum after urinating or defecating is possible only from front to back;
- Thoroughly wash the hands before visiting the toilet;
- Do not use sponges to wash your perineum;
- Use only liquid soap to prevent breeding of bacteria in bar soap;
- When taking a shower, the first thing you need to wash is the area around the urethra.
For antibiotic treatment the drugs of penicillin, cephalosporin, sulfanilamide and nitrofuran group are used. Duration of therapy is usually 14 days. Second-line drugs include fosfomicin (monural). The selection of the drug, the frequency of administration, dosage and duration of administration is determined by the attending doctor.
Urinary tract infections are often associated with pregnancy. They are one of the most frequent complications during pregnancy. It has been proved that infections can be the cause of various pathological conditions: prematurity, intrauterine growth delay in children, congenital anomalies and increased perinatal mortality risk.
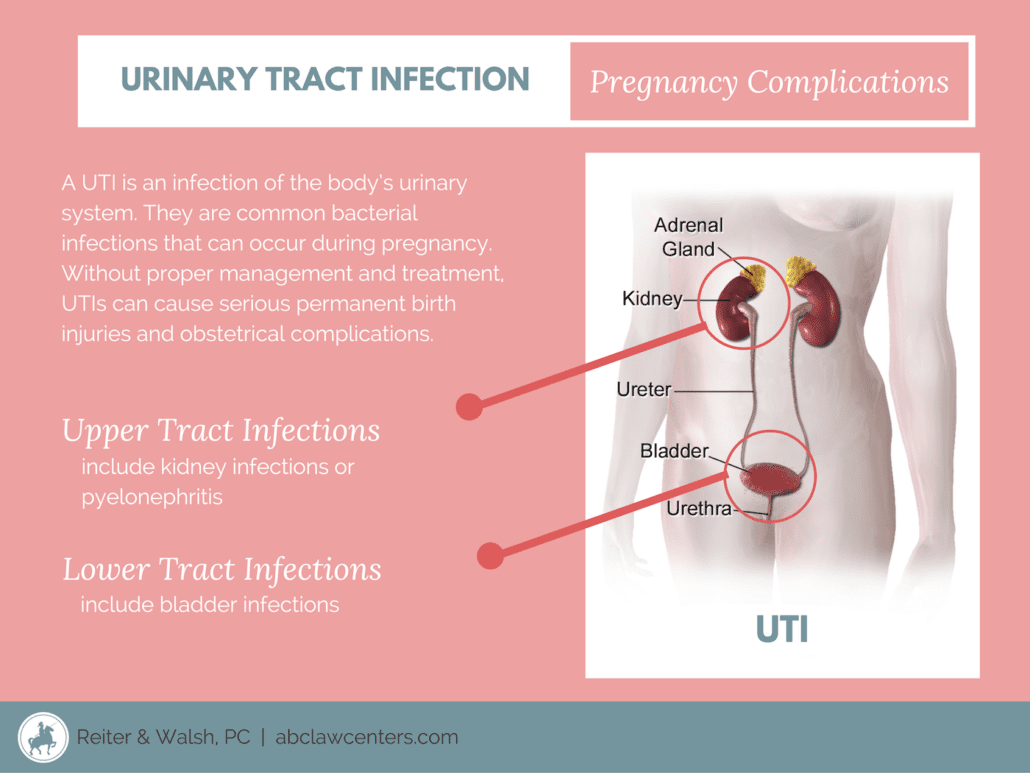
Urinary tract infections are divided into three groups:
- bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in the urinary tract;
- infections of the lower urinary tract sections (cystitis, urethritis);
- infection of the upper urinary tract sections (pyelonephritis).
Women have pyelonephritis 5 times more often than men, and in normally happens in the reproductive age. Why? Partly because of anatomical features of the female body: a short and wide urethra opening near the vagina (i.e. high chances for the invasion of different infective forms). In addition, the physiological changes that are happening in the urine-excretory system of women during the second phase of the menstrual cycle, also reduce resistance to infection.
It is established that the risk of developing a urinary tract infection is higher among the women who:
- for the first time gave birth in the age of over 28-30 years;
- gave birth several times;
- have already had these diseases;
- women with diabetes;
- have anatomical abnormalities or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract.
As you know, the kidneys experience great stress during pregnancy – they are constantly tightened. They have to remove the products of decay not only from the woman’s body, but also from the body of the growing fetus. However, the pregnancy itself does not cause any changes in the kidneys and they are able to function properly. In the last months of pregnancy the presence of traces of protein can be observed in the urine- this is the first signal of a possible gestosis.
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria

It is detected in the urine analysis of 2-7 % of pregnant women, although clinically is not visible (and therefore referred to as "asymptomatic"). The diagnosis means that there is a persistent bacterial colonisation in the urinary tract. Despite the lack of clinical picture, asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy is quite common (in 20-30 % of cases), provokes cystitis and pyelonephritis and requires specific treatment.
Acute Cystitis
This type of urinary tract infection during is easily detected with typical manifestations of acute inflammation: frequent, painful urination. Many remedies for cystitis are now available. You can, of course, stop the inflammatory process. However, you should not do this, especially when you are pregnant. When treated improperly, the acute cystitis easily becomes chronic. In addition, as with asymptomatic bacteriuria, the infection may go straight to the kidneys and cause pyelonephritis.
Acute Pyelonephritis
When infection-induced focal destructive inflammation occurs, the interstitial tissue of kidneys and the pelvicaliceal system are damaged. This is very serious complication of pregnancy (also referred to as gestational pyelonephritis). Can progress up to the development of urosepsis and lead to premature birth.
It occurs in more than 12 per cent of cases (more often during the first pregnancy). If often has an adverse effect on the course of pregnancy and the child, is often accompanied by gestosis, may cause spontaneous abortion, fetal malnutrition development, chronic placental insufficiency.
Causes and Activators
The two group of factors have major impact on the development of urinary tract infection — anatomical and hormonal. Starting with the seventh week the physiological gidroureter is formed – the extension of the pelvicalyceal system and the ureter. Thus, the body tries to adjust to the increased amount of circulating fluid. The volume of the ureter may reach 200 ml which may cause the disruption of urine outflow, and its engorgement in the ureter that is favourable for the emergence of bacteriuria.
The uterus gradually increases in volume, changing the position of the bladder deforming and compressing it. An anatomically close distribution of ureter and vagina, as well as the relative gluko-zuria (sugar in the urine) makes the infection spread easier. An elevated estrogen level causes decrease of ureteral peristalsis that may contribute to the disruption of urine outflow.
All these changes during pregnancy can begin aroud the 8th week and reach its climax at the 18-20th week, manifesting itself for 2-3 weeks after birth. By the beginning of the second half of pregnancy the disruption of the urine passage may occur because of th squeezed ureter and increased in size and shifted to the right uterus. The thicker and shorter right ovarian varicose vein may also compress the ureter. These facts explain the dextral pyelonephritis.
The leading cause of urinary tract infections that affects both pregnant and nonpregnant women is escherichia coli (80-90 % of cases), but there may be other gram-negative bacteria such as proteus and klebsiella. Gram-positive bacteria encounter much less frequently. Candida may cause the inflammation process in kidneys during pregnancy. A significant role in the occurrence of pyelonephritis also play mycoplasma, ureaplasma, trichomona, 20 % of patients have identified microbial associations.
Endotoxins of colon bacteria cause sclerosis of the renal pelvis wracks kidney capsule and paranephric body. Infection caused by proteus, is distinguished by recrudescent nature, stones formation and a lower content of leukocytes in the urine due to their destruction by microorganisms. Gestational pyelonephritis caused by gram-negative flora is the heaviest, distinguished by bacterial shock and hematocepsis.
How Does Pyelonephritis Manifest Itself?
The clinical picture of the disease is directly affected by the bacteria path. If it is hematogenic (with the blood flow), the disease manifest itself through the common symptoms. If it is urinogenous (through the urine) then the local symptoms dominate. Manifestation of acute pyelonephritis usually occurs a few days after exacerbations in chronic tonsillitis or identifying other focal infections (furunculosis, mastitis, etc.). That is why the disease is difficult to diagnose properly. The symptoms are sudden fever, chills, profuse sweating, headache, severe pain in the lower back, usually on the right.
The most typical cases are characterized by the triad of symptoms: shivering, dysuric manifestations and pain in the lower back. Pain tend to increase and every new rise in temperature is associated with new purulent formations in the kidneys. A woman is bothered by nausea, vomiting, body aches all over her body. Tachycardia and shortness of breath are also common. The bacterial shock can develop with blood pressure lowering.
Treatment of Acute Pyelonephritis
It is always complex, long-lasting (4-8 weeks), individual. Things to take into account when prescribing the drug therapy: the stages of pregnancy, the severity and duration of illness, the analysis of the functional state of the kidneys and liver, individual tolerance of drugs and the possibility of their transition into the milk. In the acute stage of the disease a woman should stay in bed — for no less than 4-6 days. When the fever passes, it is recommended to stay active to improve the outflow of urine.
The use of positional therapy: 2-3 times a day a woman should stay in the knee-elbow position for 4-5 minutes; sleep only on the opposite side of the infected kidney. A special diets with salt restriction is not required. If there is no swelling, drinking of up to 2 litres per day is prescribed. We recommend the cranberry juice, kidney tea, infusions of parsley, horsetail, cowberry grove – herbal diuretics and antiseptics. There are ready-made medicinal herbal drugs (primarily canephron) that have immense value in treating pyelonephritis and other urinary tract infections.
Lately plant extracts with a complex action such as Canephron (Bionorica AG, a german pharmaceutical company) are widely used. It has antiseptic, antiinflammatory, antispasmodic, antibacterial and diuretic action. Canephron is used to treat gestational pyelonephritis in early stages of pregnancy. It helps to prevent exacerbations of chronic pyelonephritis, treat urolithiasis, prevent pregnancy complications that entail violations of functional condition of kidneys. Canephron is suitable when antibiotic is cancelled during treatment of resistant infections of the urinary tract and also good for long-term use after initial treatment with antibiotics. The drug does not have side effects.
Effects of Infections
The women who suffer pyelonephritis demonstrate some distinctions during pregnancy and childbirth. 6 % of women with chronic pyelonephritis are exposed to the late miscarriages, 25 % are at risk of preterm birth, 44-80 % have late toxicosis. Pregnancy and fetal development in defining the extent depend on the severity of the descreased kidney function and infection symptoms.
The born children often have a number of signs of infection received in-utero. Thus, kidney pathology that mother has tend to influence the development of kidneys of her child (not enough mature renal tissue, dysmerogenesis of the urinary system). The fetal hypoxia and oligotrophy are also common, and therefore, there is a need for careful monitoring of the fetus.
In the postpartum period about 22-33 % of women who have had gestational pyelonephritis, have purulent-septic diseases. At the 4th and 12-14th day after birth the pyelonephritis may worsen. In 20 % of cases the renal function may remain low post partum.
Prevention of Urinary Tract Infections During Pregnancy
- Preparing for pregnancy. It should be thorough and meticulous, especially if the woman had urinary tract infections in the past. The doctor will suggest the tests both spouses should undergo before conceiving a child.
- Early rehabilitation of all centers of infection in the body.
- Pregnant woman should embark on dispensaries in female consultation as soon as possible and follow medical advice throughout the pregnancy, undergo medical tests and other surveys. Try not to get cold!