Tuberculosis In Pregnancy

Contents:
- Symptoms of Tuberculosis During Pregnancy
- Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Pregnant Women
- Danger to a Fetus
- Treatment of Tuberculosis During Pregnancy
- Childbirth and Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis During Pregnancy
Tuberculosis is an infectious diseases caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The main transmission route of this disease is an airborne one, that’s why tuberculosis usually affects the respiratory system.
Most people carry Mycobacterium tuberculosis in their body, but only the influence of various adverse factors causes this disease to start and progress. Pregnant women in this situation aren’t the exception: their hormones change along with their physical condition and so they (as many other people) become vulnerable to this disease. Usually the symptoms of tuberculosis appear in the first trimester, less often – in the second half of pregnancy.
There are additional risk factors that could lead to the development of tuberculosis in pregnant women:
- alcohol and drug addiction;
- bad living and social conditions;
- violation of the nutrition;
- presence of people sick with tuberculosis in closest environment.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis During Pregnancy
In the first half of pregnancy women often confuse symptoms of tuberculosis with ordinary illness and toxicosis. Weakness, malaise, slight fever and constant coughing don’t disturb pregnant woman at first, and in the meantime inflammatory and destructive processes develop in her lungs.
In the second half of pregnancy symptoms of tuberculosis are usually less obvious, because inflammatory process reduces and destroyed parts are replaced with connective tissue. But in some cases the body fails to overcome the infection and so mycobacteria can spread throughout the body, affecting the abdominal organs along with bone and lymphatic systems.
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Pregnant Women

A high risk of tuberculosis development accompanied by constant coughing can be suspicious: maybe a woman has pulmonary tuberculosis. In this case a pregnant woman takes a Mantoux test, which is absolutely harmless both for mother and for fetus. Identification of mycobacteria in sputum and lesions on chest radiographs allow diagnosing definite tuberculosis. Protective apron is covering a belly of a pregnant woman during the X-ray to reduce a radiation effect on a fetus.
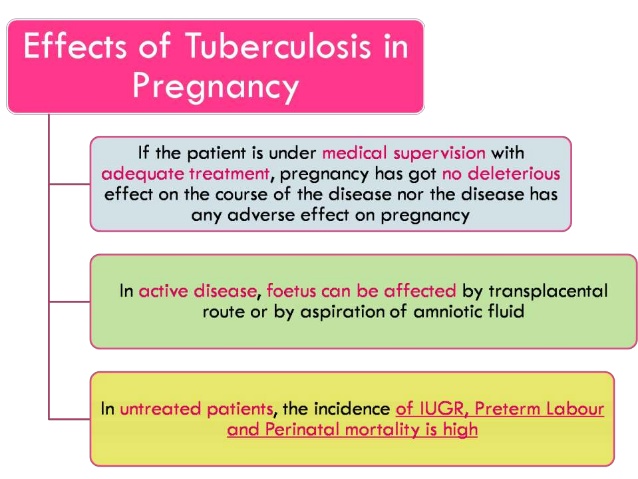
Danger to a Fetus
A pulmonary tuberculosis is harmless to a fetus in mother’s womb. But if a woman is diagnosed with extrapulmonary tuberculosis, a risk of fetus infection increases. It is believed that a placenta barrier is impermeable to mycobacteria, that’s why babies are usually infected during childbirth.
But in some cases a baby can still be born with tuberculous lesion of its internal organs. A mother suffering from active form of tuberculosis is isolated from her child after the childbirth due to a high infection risk.
Treatment of Tuberculosis During Pregnancy
If a woman is prescribed with tuberculosis treatment, her chances of giving birth to a healthy baby grow higher (though there’s still a possibility that this disease will affect the fetus badly).
After the illness is confirmed with the help of tests, the doctors prescribe antimycobacterial drugs (at any stage of pregnancy). The treatment is prescribed individually for every patient.
Childbirth and Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis isn’t a pathology that requires special approach to a childbirth. That’s why a doctor’s decision about the method of birth is usually based on obstetric indications only. A severe form of tuberculosis, accompanied by strong cardiovascular and/or multi-organ failure is an exception, though.
Video: Tuberculosis & Pregnancy, TB can Lead to Infertility.