Pneumococcal Vaccine
Contents:
Pneumococcal infection is the whole number of diseases which are caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae (it is translated as pneumococcus). Pneumonia, acute otitis, purulent meningitis, endocarditis, pleuritis, arthritis — all these diseases are rather serious and hazardous to child’s health, threatening with possible complications and irreversible processes for the future.
This bacterium usually becomes active after other previous illnesses, such as flu, measles, otitis and even usual cold. The best prophylaxis in this case is a well-timed pneumococcal infection inoculation at children’s age. Parents can express their willingness in written form or refuse it.
Vaccination Terms
According to researches, risk to catch an infection is very high in children aged about 24 months of life. According to a calendar of inoculations, the time frame established for that purpose in the following way:
- 3 months;
- 4,5 months;
- half a year;
- 1,5 years — revaccination.
At the same time the preparation can effectively and absolutely safely be combined with other injections, with the exception of BCG vaccine. If the above parameters are observed, pneumococcal vaccine allows forcing immunity in little children already under 2 years of age, when the bacterium Streptococcus pneumonia is most active and dangerous.
After such immunization, even if the child would be ill becoming infected, the infection will occur in mild form and without further complications. So parents are hardly worth refusing this inoculation. Even more, as it doesn’t practically cause any response.
Reaction To The Inoculation
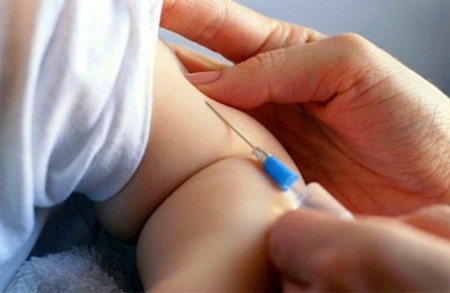
A pneumococcal vaccine has no special side effects in children. All symptoms which can arise after the inoculation are rather typical, as well as after other bacterinations. In the first 2–3 days after this procedure parents can notice the following implications in the child:
- at the point of injection (for the children under 2 years of age, that is the femur surface, and for the older children – is the medium third of the upper arm. The vaccination is administered intramuscularly) there may be a hardening and a typically reddening of the skin, and the child might have cried because of emergence of painful feelings in this place;
- slight increase of temperature — happens extremely seldom;
- flatness, drowsiness (or, on the contrary, sleeplessness), irritability, refusal of food, tearfulness;
fever.
All these side effects after the pneumococcal vaccine inoculation need just to be endured. But first, they happen rather seldom (local reaction — in 5% cases, high temperature — in 1%). Secondly, they very quickly pass – may be, even within a day.
It is very important to provide the correct care of the place of the vaccine introduction. And that’s not the point about water procedures at all. On the contrary, it is possible to wet this place. But it is strictly forbidden to smear it, to process it with brilliant green, iodine or other antiseptics. And it isn’t recommended to apply compresses or plasters, too.
In case of high temperature (if it exceeds 38 °C) it is possible to give an antipyretic febrifuge, permissible for children. In case of slackness and irritability it is necessary just to pay to the child as much as possible attention. If above-mentioned symptoms don’t pass and the condition of the child’s health is only aggravated, immediately report about it to the pediatrician, who is keeping you under observation. Perhaps, one of contraindication to vaccination against the pneumococcal infection was missed.
Contraindications
One of indisputable benefits of pneumococcal vaccine for children is its good tolerance and a minimum of contraindications. The vaccination of a child is seldom postponed due to some medical indications. Most often such child remains without the injection only because of refusal of parents. Contraindications to such vaccination are:
- an individual intolerance of the administered preparation, allergy to one of its components – it happens extremely seldom: in this case, if the child’s organism reacted to the first inoculation very violently, all the subsequent injections ought to be cancelled;
- acute course of any disease, even usual cold;
- exacerbation of any chronic illnesses;
- raised body temperature (even through insignificant, till 37 °C), even if inspection didn’t find its obvious reasons.
In the presence of three last contraindications, the pneumococcal inoculation is temporarily postponed until the absolute recovery. Before introducing this injection, the doctors conduct examination of the children with the object to: whether they are ill at the moment of inoculation, and whether they have high temperature, what chronic diseases are diagnosed, and how the child’s organism reacts to the previous vaccine. Only after that they can come to a conclusion that the vaccination is possible or it must be postponed till better times. Many parents write refusal only through fear of complications. But whether they are really so terrible?
Possible Complications
Really, as well as after any vaccination, complications after the pneumococcal vaccine are quite possible. The question is that they are noticed extremely seldom, usually in case of the severe form of an allergy, or neglect of some other medical factors. The doctors bear the responsibility for the child’s condition at the time of vaccination therefore they try to expose all problems with child’s health before introduction of the injection responsibly and with all their skill. Non-compliance with contraindications could give rise to such consequences as:
- quincke’s edema owing to serious allergic reaction to one of components of the entered injection (except polysaccharides, which are the main active ingredients, “Prevenar” includes aluminum phosphate and sodium chloridum; “Pneumo-23” includes phenolum as preserving agent, and also sodium chloridum and sodium phosphate);
- exacerbation of the available chronic diseases;
- sharp aggravation of symptoms in the presence of sharply proceeding infections;
ultraboundary temperature increase if the child already had a fever at the time of vaccination.
These are the most terrible complications which are possible after the pneumococcal vaccination. However they are extremely rare and they can be avoided, keeping contraindications for carrying out similar bacterination.
Effects from previous pneumococcal acute otites, pneumonia, purulent meningitis, endocarditis, pleurites and arthritises are diagnosed much more often and leave irreparable mark on the child’s health for the future. It is far easier to carry out preventive measures for prevention of such horrible diseases, than to have a long and painful convalescence after them. Today the pneumococcal vaccine remains one of the most effective preventive ways to avoid such infection.
Video: Pneumococcal Vaccines. Bulletpoint