Mononucleosis In Children
Contents:
- The Symptoms Of Mononucleosis In Kids
- Diagnosing Mononucleosis In Babies
- Treatment Of Mononucleosis In Children
- Prevention And Consequences Of Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis is a disease that is accompanied by an increase of body temperature, increased size of lymph nodes, fever and tonsillitis. In the Soviet literature this disease was called the Filatov’s disease at that time. The thing is that this was exactly Filatov who was the first to describe the characteristic features of infectious mononucleosis in 1885. The disease is caused by a herpes virus type.
The main source of the infection is a man himself. However, this infection is also airborne. A person may become infected with it through cough, sneeze, through saliva (for example, when kissing). It’s also important to mention that there are cases of local outbreaks of the disease at schools and kindergartens described. Those were cases when the virus was passed on to another person through a toy both he and the infected person used or through handset. Besides, sometimes, this disease is called the kiss disease in literature since earlier mononucleosis, as a rule, was passed on from one person to another in case they kissed.
Children in general and ones in their teens are more prone to the disease. In case of children who are not older than 10 years old, the disease is rarely to be diagnosed since the symptoms are suppressed and there is only a slight increase of temperature and general malaise. In case of children who are in their teens, the course of infectious mononucleosis quite often lasts for several months.
The Symptoms Of Mononucleosis In Kids
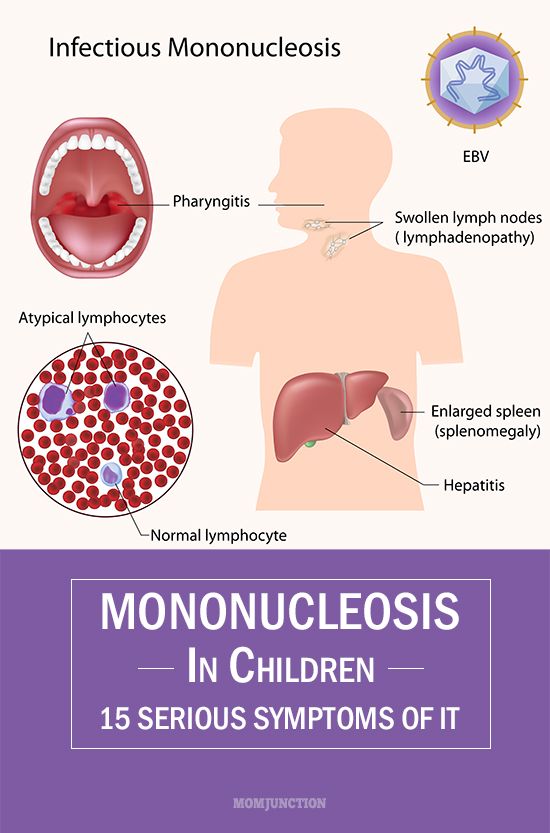
The list of the disease’s main symptoms includes:
- the appearance of the headache;
- the increased size of liver and spleen;
- mononuclear tonsillitis (there are dirty-grey pellicles on the tonsils. They are easy to remove with tweezers.);
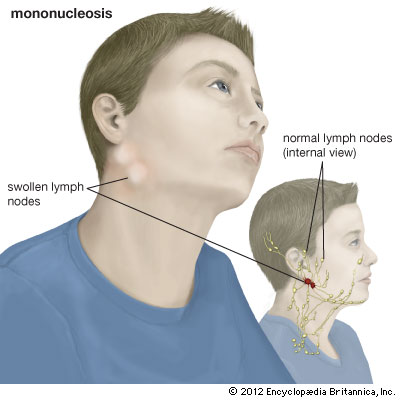
- the inflammation of lymph nodes;
- the increased size of lymph nodes (as a rule, these are the lymph nodes on the side back area of the neck that get increased in size. They twist in aggregations or turn out to be chain-like. In case of neck palpation, there are painful sensations. The lymph nodes are not connected with the surrounding tissues and, sometimes, their size increases up to the size of an egg.);
- pain in muscles and joints;
- fever;
- weakness;
- high susceptibility to provocative agents of other infections;
- the skin is very often affected by herpes;
- bleeding of gums;
- loss of appetite;
- cold in the nose;
- pains in the throat;
- stuffy nose;
nausea.
It’s important to mention that the course of the disease may go slowly and flabbily. That’s why, for a long period of time, a child may only suffer from a severe fatigue. Consequently, he or she will constantly say he or she needs rest and sleep.
In case of this disease, there are non-characteristic mononuclears found in blood. They are a 100% proof that a child has infectious mononucleosis.
Diagnosing Mononucleosis In Babies
Diagnosing the disease is quite hard due to the fact that its clinical picture is quite typical to many other virus diseases. The main symptom that allows to suppose a child is having an infectious mononucleosis is the fact that the symptoms do not disappear for quite a long time.
Once the supposition is pointed out, a doctor refers a child to make 2 blood tests. The aim of the first test is to detect heterophile agglutinins in blood. The test turns out to be positive in 90% of cases. The second test is the analysis of blood smear so that to find non-specific lymphocytes.
In rare cases, there is a need to differentiate infectious mononucleosis from tonsillitis, diphtheria, rubella, lymphogranulematosis and HIV.
Treatment Of Mononucleosis In Children

In cases when the course of the diseases goes quite smoothly or medium-hard, there is no need to admit an ill child in the hospital. The treatment may be carried out at home. In this case, a child should keep up to bed rest and follow the doctor’s recommendations. A special diet (table №5) is prescribed only if liver and spleen are increased.
It’s important to point out that at present there is no specific treatment of the disease exists. The therapy includes:
- eliminating the organism’s intoxication;
- rinsing throat with bactericidal agents;
- taking general health-improving drugs;
- taking preventive measures against allergic reactions (there are desensitizing drugs prescribed);
- taking antipyretic drugs (if necessary).
- In order to keep the fever down it’s recommended to take only paracetomol and its analogies. Aspirin is strictly forbidden (this refers also to children younger than 18 years old since it may cause liver and brain damage).
- In case of mononucleosis, warming up is also forbidden since it makes the general condition only worse.
- Speaking about other limitations in diet, they include fat, smoked and sweet foods. It is recommended to eat fresh fruits and vegetables, drink dairy products with low percent of fat in them, eat porridges, fish, boiled meat and soups.
- Garlic, onion, ice-cream and leguminous plants are forbidden.
- A child is to stick to the diet for half a year after he or she has recovered from the disease.
- It’s necessary to limit physical loads since they may lead to the spleen’s rupture.
- In order to be able to breathe in through nose drops with ephedrine decoction are to be used (5 times a day).
- In rare cases, an operation on removing spleen (splenectomy) is carried out as a kind of symptomatic treatment. It is rational to carry it if the size of the spleen and its functioning are increased. In this case, frequent recurrences of the disease happen.
Prevention And Consequences Of Mononucleosis
There is no separate set of preventive measures against mononucleosis in children at present. Doctors recommend sticking to the rules that are given in case of acute respiratory viral diseases.
Non-specific preventive measures include improving the capability of immune system and general sustainability to various diseases.
In the majority of cases, infectious mononucleosis in case of children ends with a child being fully recovered. It’s only in rare cases that complications of the disease occur. Such like complications and consequences include:
- neurological complications (meningitis, mental disorders, encephalitis and polyneuropathy);
- fever syndrome;
- uveitis;
- pneumonia;
- spleen’s rupture (it is accompanied by the decrease of blood pressure, loss of consciousness, a strong and sharp pain in the belly);
- hematological complications (the decrease of the leucocytes amount, death of erythrocytes, decreased number of thrombocytes).
Besides, mononucleosis may be complicated by one more, other pathology that is caused by streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus organisms, etc. There is also a possibility of the tonsils overlapping the upper respiratory tracts. In rare cases, mononucleosis leads to a two-sided infiltration of the lungs and severe oxygen hunger and severe case of hepatitis.