Ear Infections During Pregnancy
Contents:
- Peculiarities of Ear Infection in Pregnancy
- Symptoms and Diagnosis of Otitis Media
- Traditional Treatment
- Folk Remedies
- Things to Avoid
- Prevention
Ear Infections in Pregnancy
Any infectious disease in pregnant women is a problem. As you can’t have a full-fledged treatment and take all the necessary medications, while the harm from bacteria and viruses is significant, you’d better think in advance about the prevention of ENT diseases and other diseases in pregnancy. Unfortunately, not everybody manages to avoid such illnesses. Ear infection is one of the most common pathologies that many women face during their pregnancy.
Peculiarities of Ear Infection in Pregnancy
Otitis media is an inflammation of the ear that can have a different course depending on the localization of inflammatory changes. The ear is composed of external, middle, inner portions. The names of ear infections derive from the names of ear portions: otitis externa, otitis media and otitis interna (labyrinthitis). Otitis externa is characterized by inflammation of the auditory canal, the auricle and the tympanic membrane. Otitis media affects mainly the mucosa of the tympanic membrane and the auditory tube. The middle ear is composed of the mastoid air cells and the temporal bone. If the disease spreads in this area, it’s considered that otitis is complicated by mastoiditis.
The most serious disease is labyrinthitis, or otitis interna. The inner ear in addition to the cochlea (sound analyzator) includes vestibular receptor, that’s why otitis interna in pregnancy may provoke vestibular failures and impact the auditory function. Otitis externa is considered the safest from the point of view of consequences, while most commonly pregnant women suffer from catarrhal otitis media and suppurative otitis media.
In most cases otitis is caused by the reduced immunity in a pregnant woman, as the body gets more vulnerable to infections. As a result, the slightest head or ear cooling contributes to the development of the first symptoms of the disease, as bacteria start multiplying in the outer and middle ear.
Viral infections may also contribute to the development of otitis in pregnancy. If you are prone to ear pathologies, you may have unpleasant otitis consequence of ARVI. Flare-up of other chronic ENT diseases such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis may have the same effects, because all these organs are interconnected, and the infection can freely travel from the nasopharynx, nose and throat to the ear through the auditory tube. If a woman has such problems as a deviated septum, hypertrophy of nasal turbinates or polyps, somatic illnesses, risk of ostitis in pregnancy will be even higher.
The negative impact of the disease on the fetus is clear: all viral infections have negative consequences while some of them are able to penetrate the placental barrier, impede the normal development and cause hypoxia. Infectious diseases can provoke miscarriage, premature birth and bring other problems. Fortunately, if you seek medical advice at early stages and are assigned with a proper treatment, the disease will not spread to other body’s zones or cause any complications as it will stop at the local level.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Otitis Media

Otitis may harm both the baby and the expectant mom. Without adequate therapy it often becomes chronic, and regular flare-ups lead to hearing loss.
Most patients with otitis have the following symptoms:
- severe pain in one or both ears;
- fullness of the ear;
- noise in the head;
- itching, irritation in the ear canal;
- fluid drainage from the ear;
- hearing impairment;
- general malaise;
- increase in the body temperature;
- weakness;
- lymphadenitis.
Usually a sharp shooting pain is typical for the initial stage of otitis media. In few days without adequate therapy it grows out to the purulent form. The tympanic cavity filled with purulent fluid puts pressure on the eardrum that finally collapses. After that, the pain remits and the auditory passage is filled with pus and sometimes blood. The eardrum’s perforation gradually heals, the hearing improves or fully restores.
Above we have described symptoms common for ordinary people, but they may vary in pregnant women. Most often at the beginning, otitis has a suppressed form, but sometimes it develops quickly accompanied by malaise, but featuring no local manifestations. In some cases, a pregnant woman with destruction of ear tissues had normal body temperature and felt herself well.
Diagnosis of otitis media in pregnant women includes otoscopy, microbiological test of ear smear. If necessary, a woman is assigned with hearing tests (camertonal test or audiometry), auditory tube function testing, endoscopic examination of nasopharynx etc. Radiography and CT in pregnant women are strictly forbidden, and in acute need a woman can be assigned with MRI, starting from the second trimester of gestation.
Traditional Treatment
Selecting treatment for a pregnant woman the doctor should keep in mind that benefits from the use of drugs should be greater than the potential danger. In other words, you shouldn’t run excessive risk – otitis in pregnancy should be treated by the safest means. At the initial catarrhal stage of otitis, when the eardrum isn’t perforated yet and there is no pus, you can be appointed with local anti-inflammatory ear drops such as Otipax or Otinum. At the advice of your doctor you can insert in the ear heating turundas soaked in vodka or spirit to reduce inflammation.
In case of suppurative otitis externa (a boil in the ear canal), the boil is removed and the ear is sanitized with anticeptics suitable for pregnant (Miramistin, for example). In case of a strong swelling of the auditory tube it’s necessary to use vasoconstrictor drops in children dosages (Nazivin, Ximelin). If the inflammation of the outer ear can turn into otitis media, you can be appointed with local antibiotics drops (Sofradex, Sulfaсyl sodium).
You can also be prescribed with penicillin antibiotics such as Amoxicillin, Flemoxin. If you have a large amount of pus, the doctor in his office will puncture the eardrum and sanitize the outer ear with swabs soaked in spirit, hydrogen peroxide or antiseptics. Blowing of the auditory tube, pneumomassage of the eardrum within 7-14 days are also of help and are absolutely safe for both the woman and the fetus.
Folk Remedies
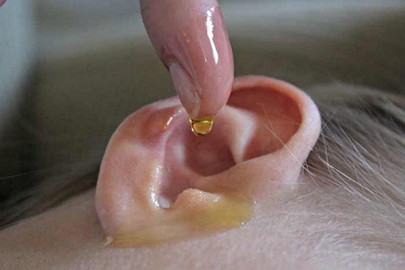
You can complement the traditional therapy prescribed by your otolaryngologist by effective folk remedies:
- Boil in 300 ml of water a pack of fine cut bay leaf for 10 minutes. Leave the infusion for two hours, then drain. Apply warm to rinse the ear.
- Squeeze juice of aloe and kalanchoe, mix them in equal parts. Soak a gauze turunda in this solution, insert it in the ear and leave for an hour. Repeat twice a day.
- Cut the fresh leaf of geranium, roll it into a tube and inserted into the ear. Keep geranium in the ear for 1-2 hours. Squeeze it with your fingers before you put it in the ear.
- Join propolis tincture (1 part) and vegetable oil (2 parts), put 5 drops of solution in each ear, cover their ears with cotton wool and leave the medication in auditory canal for 15 minutes.
Any folk treatment should be applied only after the diagnostics and receive the approval of your physician.
Things to Avoid
Healing will come faster if the woman follows all the doctor's advice. Do not arbitrarily reduce the length of the therapy or change medications without taking the doctor’s advice. It is strictly forbidden to warm the ear or do compresses before you see your doctor, because in case of suppurative otitis this may lead to serious complications. Some medications on the stage of perforation may cause big problems if they get into the tympanum or in the inner ear. These include alcohol, anti-inflammatory medications and many others. There are dangerous, toxic medications banned for the use in pregnant women to treat otitis (Anauran, Normax, Cipromed etc.)
Prevention
Since otitis is often the consequence of a viral infection or hypothermia, to prevent it you need to avoid flu and colds, dress for the weather and cover your head with a hat. Even before the pregnancy, you should strengthen immunity, which requires more walking, eating properly, exercising and fortifying yourself against colds. Taking a bath or a shower avoid penetration of water into the ear canal as it contributes to reducing the local immunity and often causes otitis.