Cervix During Pregnancy

Contents:
- Your Cervix During Pregnancy
- What is the Uterine Cervix?
- Uterine Cervix After an Impregnation
- Normal State of the Uterine Cervix During Pregnancy
- Cervical Incompetence During Pregnancy
- Endocervicitis of the Uterine Cervix
- Cervical Erosion During Pregnancy
Your Cervix During Pregnancy
During the first visit to the doctor, the pregnant woman has to undergo the gynecological exam, which will allow to not only confirm pregnancy and set its term but also to evaluate condition of the woman's inner genitals. Among them, the special attention is given to the uterine cervix.
What is the Uterine Cervix?
It is an original connecting tube between the uterus and the vagina, the length of which is approximately 3-4 cm and its diameter is about 2,5 cm. There are two parts of the uterine cervix: the bottom and the top ones. The bottom part is called vaginal, because it extends into the cavity of the vagina, and the top part is called supravaginal one, because it is located above the vagina. The cervical canal is located inside the uterine cervix; it is opened into the cavity of the uterus by its internal orifice. Outside the surface of the uterine cervix has pinkish tint, it is smooth and shiny, strong and inside, it is bright-pink, velutinous and loose.
Uterine Cervix After an Impregnation
During pregnancy, a number of changes occurs in this organ. For example, its color changes sometime after a fertilization: it becomes cyanochroic. The cause of this is in extensive spider veins and its blood supply. At the same time, the cervix glands dilate and become more branched.
In the 9th month of pregnancy, the physician notes uterine cervix tissues' becoming flexible and its «maturation». These changes in an organism of a pregnant woman indicate readiness for the birth of a child. Immediately before the labor, the uterine cervix shortens (to 10-15 mm) and locates in the center of the small pelvis. According to the revelation of the channel of the uterine cervix, the gynecologist obstetrician determines the approach of labor activity, which begins with enlargement of the internal orifice and contractions.
Normal State of the Uterine Cervix During Pregnancy
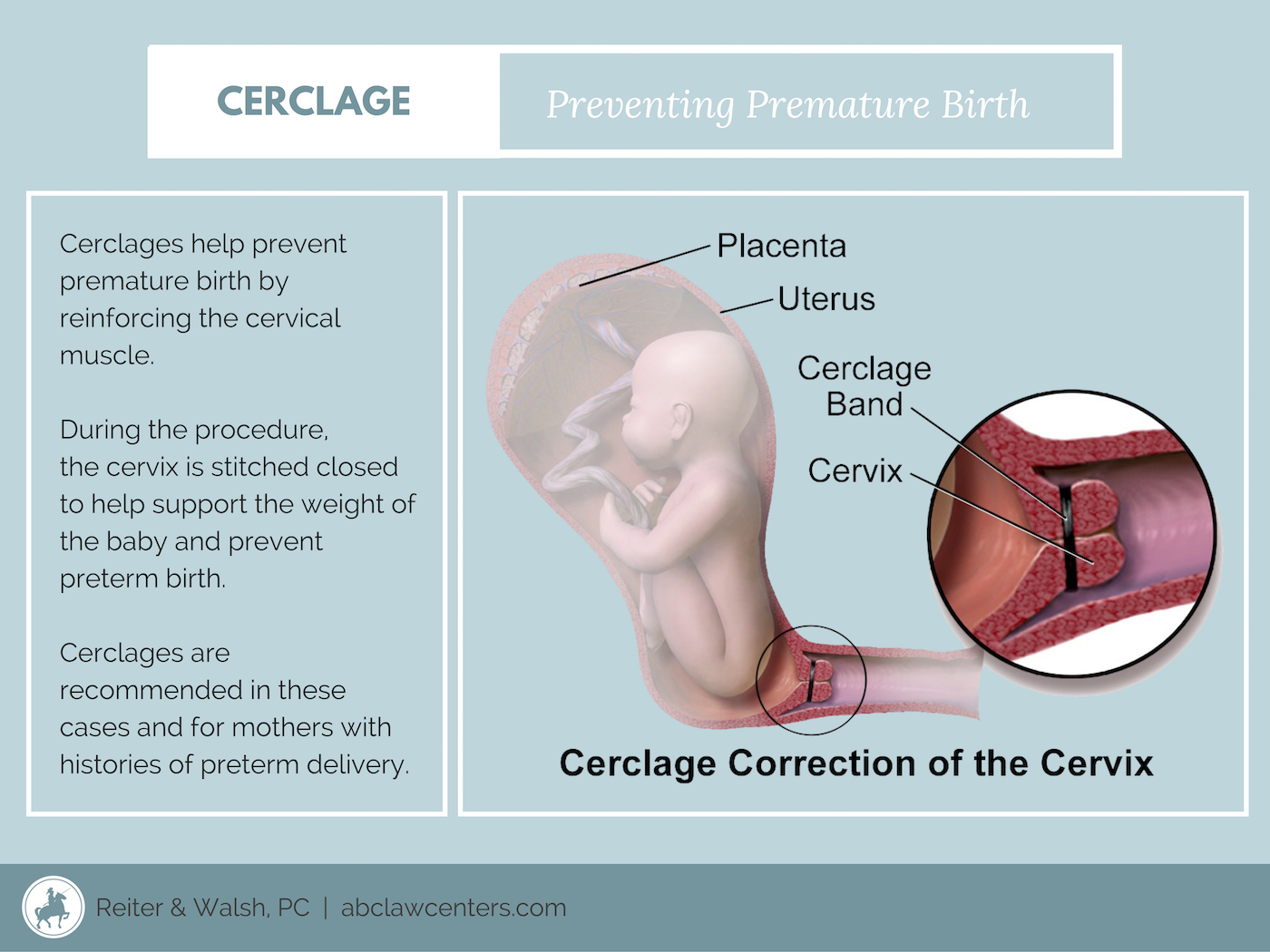
During 9 months, the woman is forced to frequent a gynecologist. In other words, in healthy pregnancy, in the best variant without complications, it happens 9-12 times at a minimum. If there are health problems or risk of miscarriage, this number can be several times greater. By the first examination, the physician searches out the uterine cervix and determines its form, extent, consistency and location. In normal pregnancy, the uterine cervix has firm feel and is bent back, at the same time, the channel is impenetrable for a finger. If there is any threat of the spontaneous abortion, the physician will determine this from the uterine cervix having become shorter and soft, at the same time the channel opens.
Periodic visits to a gynecologist will allow to ascertain any pathology or a disease on time and take necessary measures. During examinations the doctor takes analyses: a flora smear (this analysis will help to determine an inflammatory process, discover any kinds of infection (a fungal one, candidiasis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis) and cytologic screening (features of the structure of superficial cells and cells of the cervical canal of the uterus are examined in this way, which gives a possibility to reveal various oncological diseases on the earliest stages).
If, as a rule, at first, no pathology of the woman's uterine cervix is revealed, planned surveys of the state of this organ are conducted at 20th, 28th, 32nd in 36th weeks of pregnancy. If any disorders are observed, surveys are conducted more often. Some changes of the uterine cervix state, as well as the nature of discharge can point towards possible threat of the interruption of pregnancy. The measures taken on time allow to maintain pregnancy. Let`s describe the most prevalent diseases of the uterine cervix, which can significantly affect the course, as well as the result of pregnancy:
Cervical Incompetence During Pregnancy
This is a pathological state of the uterine cervix, in which musculature in the area of isthmus of uterus does not contract. At the same time, the uterine cervix opens beforehand, which makes keeping of a fetus impossible. Just to remind you, that in healthy pregnancy, the uterine cervix is closed tight. Having no support, the fetus is gradually descending down, labor activity is increasing and the miscarriage is occurring. Late miscarriages occurring between the 20the and the 30th weeks of pregnancy are the most relevant in case of cervical incompetence. Some women's premature revelation of the uterine cervix can be accompanied by a piercing vagina pain, while other women can have it asymptomatically.
Most often cervical incompetence increases in consequence of hypoplasia of the uterus and hormone failures, but there are other causes of its emergence:
- Congenital disturbances of the structure of the cervix with connective-tissue deficiency and relative magnification of the lobe of a smooth muscle tissue.
- Congenital hypoplasia of the cervix.
- A trauma of the isthmus and to the cervix of the uterus during abortions, in case of delivery of a big fetus, while application of midwifery forceps.
Endocervicitis of the Uterine Cervix
Often this disease – inflammation of a cervical canal– becomes the cause of the spontaneous abortions and premature birth. In this case, the increased amount of mucus excretes from the cervical canal, the place of inflammation has scarlet color. As a rule, sexually transmitted infections, a streptococcus, a staphylococcus, a colon bacillus, an enterococcus, and other similar diseases become the causes of endocervicitis. The most typical symptoms of this disease are abundant discharge with bad smell.
Cervical Erosion During Pregnancy
The erosion implies pathological condition, in which the wounds form on the uterine cervix, in other words, damage of the integrity of the outer surface of this organ is observed. Cervical erosions are very often caused by inflammatory diseases, papillomavirus infection, hormone disorders, traumas from use of barrier and chemistry contraceptives. The wound itself skins over several days later, but the problem is that it skins over not by the same cells, which cover the outer surface of the uterine cervix, but with the others ones veneering the inner mucosa of the cervix. During pregnancy the erosion is not touched, but its treatment is left for a postpartum period.
The uterine cervix is the important organ while pregnancy, in an anatomical, as well as in a functional aspect. Remember, it contributes to the process of a fertilization, inhibits a hit of an infection into the uterus and appendages, helps to «carry» a fetus to birth, participates in the labor. For this very reason, the observation of the uterine cervix state during a child bearing is extremely necessary.