Bronchitis In Children

Contents:
- What is Bronchitis?
- Bronchitis in Toddlers
- Causes Bronchitis in Children
- Pathogenesis of Bronchitis in Babies
- The Classification of The Bronchitis in Children
- The Symptoms of Bronchitis
- Diagnosis of Bronchitis
- Treatment of Bronchitis
- Prevention of Bronchitis
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis in toddlers is a general inflammation of the bronchi, the air passages between the nose and the lungs. The symptoms are cough (productive or non-productive), temperature rise, retrosternal pain, wheezing and rhonchi.
Bronchitis in children is usually diagnosed with the help of the following: an auscultatory method, a chest x-ray, a blood test, a sputum examination, a pulmonary function test, a bronchoscopy and bronchography.
The treatment for Bronchitis in children consists of antimicrobial therapy, mucolytic treatment and antitussive therapy. Additionally, physiotherapy measures can be used, including inhalations, electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, therapeutic exercises, and cupping and vibration therapy.
Bronchitis in Toddlers
Bronchitis in toddlers is an inflammation of the bronchial tree that can have different etiology factors. About 100-200 children in every 1000 are diagnosed with bronchitis annually. Acute bronchitis accounts for about 50% of all respiratory diseases in toddlers.
Bronchitis can be often found in children of 3 years and younger. Babies usually suffer the most severe form of bronchitis. With a number of factors causing bronchitis, it became a popular subject of pediatrics, pediatric pneumology, pediatric allergy and immunology.
Causes Bronchitis in Children
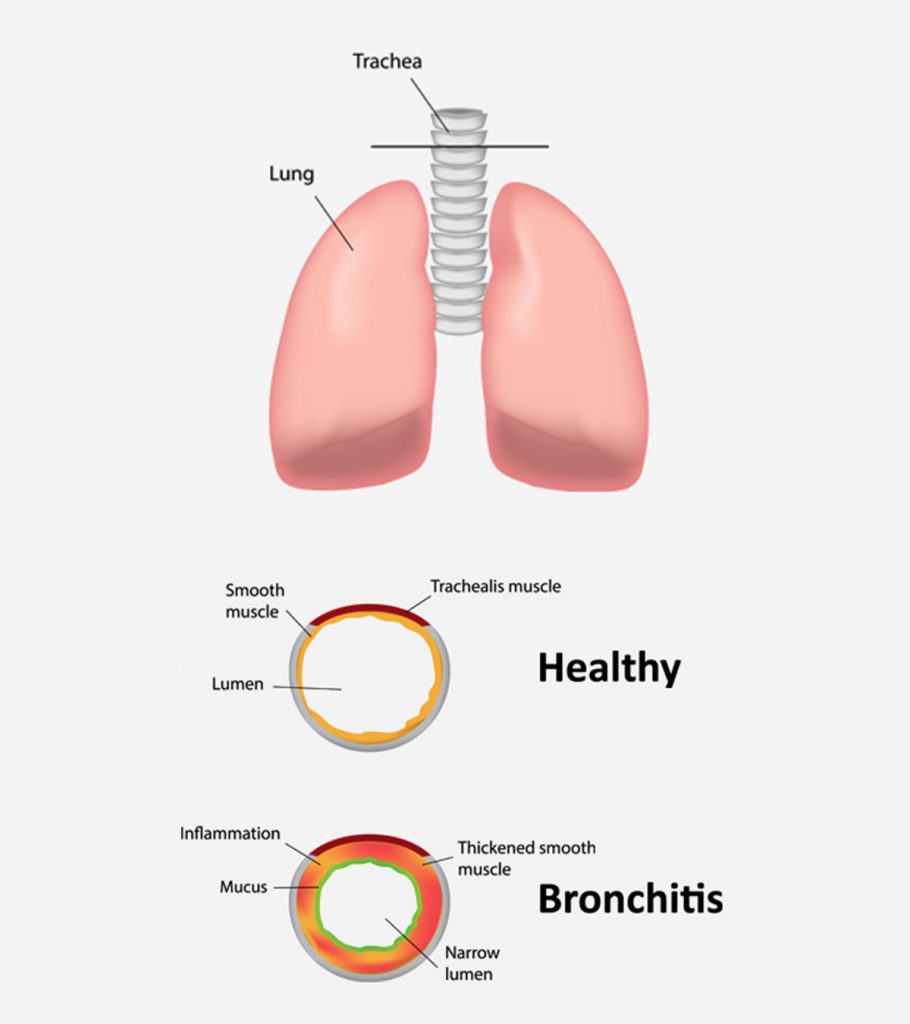
Usually bronchitis follows a viral disease, such as influenza, parainfluenza, rhinovirus, adenovirus, and respiratory syncytial virus. Less often it is caused by biological agent (streptococcus, pneumococcus, haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella, blue pus bacillus, collibacillus, and klebsiela), fungie (aspergilla and candida) and intracellular infections (chlamydia, mycoplasma, and cytomegalovirus). Sometimes bronchitis accompanies diseases like measles, diphtheria, and pertussis. Allergic bronchitis is common in children exposed to allergens entering the bronchial tree with inhaled air: dust, household chemicals, plant pollen etc. In some cases bronchitis can be triggered by the irritation of the bronchial mucosa by chemical or physical factors, such as air pollution, tobacco smoke, gasoline vapours etc.
Predisposition to bronchitis is often found in children with perinatal pathology (birth trauma, prematurity, small for gestational age, etc.), constitutional anomaly, lymphohypoplastic and exudative diathesis), congenital malformations of the respiratory system, frequent respiratory diseases (rhinitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis), a breathing disorders (adenoids, deviation of nasal septum), chronic purulent infection (sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis).
Cold seasons (autumn and winter), a seasonal outbreak of flu, childcare centers and adverse social conditions increase the chance of bronchitis epidemic.
Pathogenesis of Bronchitis in Babies
The development of the bronchitis in children depends on physiological peculiarities of the respiratory tracts: excessive blood supply of the mucosa, loose structures of the mucosa. These features contribute to the rapid spread of exudative-proliferative reaction from the upper airways to the respiratory channel.
Viral and bacterial toxins inhibit the motility of the ciliated epithelium. As a result of infiltration and mucosal edema, and increased secretion of viscous mucus, the ciliary motion gets slowed down further, which turns off the mechanist of bronchus self-purification. This leads to a sharp decrease in the drainage function of bronchi and obstruction of the outflow of mucus from the lower respiratory tract. Consequently, this creates the conditions for further propagation and spread of the infection and obstruction with the mucus of the smaller bronchi.
The characteristics of the pediatric bronchitis are significant length and depth of lesions of the bronchial wall, and the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
The Classification of the Bronchitis in Children
There are primary and secondary bronchitis in children. The primary bronchitis starts in bronchi and affects only the bronchial tree. The secondary bronchitis can be either a sequel or complication of other respiratory tract’s diseases.
Bronchitis in children can be acute, chronic and recurrent. Taking into account the extent of inflammation there are circumscribe bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchi within a single segment or lobe of the lung), common bronchitis (inflammation of the bronchi of two or more lobes) and diffuse bronchitis in children (bilateral inflammation of the bronchi).
Depending on the nature of the inflammatory response, bronchitis in children can be classified into a catarrhal, purulent, fibrinous, hemorrhagic, ulcerative, necrotic, and mixed. The most common in children are a catarrhal, catarrhal-purulent and purulent bronchitis. A special place among the lesions of the respiratory tract is bronchiolitis in children (i.e. obliterating) – bilateral inflammation of the terminal portions of the respiratory tree.
From the point of etiology one can distinguish a viral, bacterial, viral-bacterial, fungal, irritant and allergic bronchitis in children. The presence of obstructive components divides bronchitis into a non-obstructive and obstructive.
The Symptoms of Bronchitis in Children
The development of acute bronchitis in children in most cases is preceded by symptoms of viral infection: soreness in the throat, pokalyvanie, hoarseness, runny nose, the phenomenon of conjunctivitis. Soon there is a cough: obsessive and dry early in the disease, 5-7 day he becomes more soft, wet and productive with the office of mucous or Muco-purulent sputum.
In acute bronchitis in child has a fever to 38-38,5 °C (duration from 2-3 to 8-10 days depending on etiology), sweating, malaise, chest pain when you cough, in children of early age – shortness of breath.
The course of acute bronchitis in children is usually favorable; the disease ends in recovery after an average of 10-14 days. In some cases, acute bronchitis in children may be complicated by bronchopneumonia. In patients with recurrent bronchitis in children, exacerbations happen 3-4 times a year.
Acute bronchiolitis develops mainly at children of the first year of life. The course of bronchiolitis is characterized by fever, severe General condition of the child, intoxication, severe signs of respiratory distress (tachypnea, expiratory wheezing, cyanosis of nasolabial triangle, acrocyanosis). Complications of bronchiolitis in babies can be sleep apnea, and asphyxia.
Obstructive bronchitis in children usually manifests at 2-3-year life. A leading symptom of the disease is bronchial obstruction, which is expressed paroxysmal cough, noisy whistling breathing, elongated exhalation, wheezing remote. Body temperature may be normal or subfebrile.
The General condition of the children is usually satisfactory. Tachypnea, shortness of breath, participation in the breath auxiliary muscles are less pronounced than with bronchiolitis. Severe obstructive bronchitis in children can lead to respiratory failure and development of acute pulmonary heart.
Allergic bronchitis in children usually has a relapsing course. In periods of exacerbation there sweating, weakness, cough with separation of mucous expectoration. Body temperature remains normal. Allergic bronchitis in children is quite often associated with allergic conjunctivitis, rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and may go into asthmatic bronchitis or bronchial asthma.
Chronic bronchitis in children is characterized by exacerbations of the inflammatory process 2-3 times per year occurring consistently for at least two consecutive years. Cough is the most constant symptom of chronic bronchitis in children in the remission period he is dry during the exacerbations humid.
Phlegm cough with difficulty and in small quantities; it has Muco-purulent or purulent. It is noted the low and irregular fever. Chronic inflammatory process in the bronchi may be accompanied by the development of deforming bronchitis and bronchiectasis in children.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis in Children
Initial diagnosis of bronchitis in children is a pediatrician clarifying – a pediatric pulmonologist and pediatric allergist-immunologist. When establishing forms of bronchitis in children takes into account clinical data (character of cough and sputum, the frequency and duration of exacerbations features of the flow, etc.), auscultation data, laboratory and instrumental studies.
Auscultative picture of bronchitis in children is characterized by scattered dry (if bronchial obstruction – whistling) and different-sized moist rales,
In General, the analysis of blood at the height of severity of the inflammatory process revealed leukocytosis, lymphocytosis, increased ESR. For allergic bronchitis in children and is characterized by eosinophilia. The study of blood gas composition is indicated for bronchiolitis to determine the degree of hypoxemia. Of particular importance in the diagnosis of bronchitis in children is sputum: microscopic examination, bacterial analysis of sputum, the study on the CUBE, PCR-analysis. At impossibility of self-expectoration of a child is the secret of the bronchi bronchoscopy with a sputum collection.
Chest x-ray for bronchitis in children reveals increased pulmonary pattern, especially in the root zones. When carrying out spirometry, the child may be recorded moderate obstructive disorders. In the period of exacerbation of chronic bronchitis in children during bronchoscopy found widespread phenomena of catarrhal or catarrhal-purulent endobronchitis. To exclude bronchiectasis bronchography is performed.
Differential diagnosis of bronchitis in children should be conducted with pneumonia, foreign bodies of the bronchi, bronchial asthma, chronic aspiration of food, tubificidae, cystic fibrosis, etc.
Treatment of Bronchitis in Babies
In the acute period of children with bronchitis is shown to bed, rest, drink plenty of liquids, fully vitaminized food.
Specific therapy is determined based on the etiology of bronchitis in children: it may include antiviral (Arbidol, Anaferon, algire, etc.), antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides), antifungal agents.
Mandatory component of treatment of bronchitis in children are mucolytics and expectorants drugs that enhance thinning mucus and stimulating the activity of ciliated epithelium of the bronchi (Ambroxol, Mucosolvan, Bromhexine, mukaltin, thoracic fees).
When dry, racking, exhausting child coughing are assigned antitussive drugs (tusupreks, libeksin, stoptussin); if bronchial mast – aerosol bronchodilators. Children with allergic bronchitis are shown antihistamines; bronchiolitis are held inhalation of bronchodilatators and corticosteroids.
Of physiotherapeutic techniques for the treatment of bronchitis in children medicinal uses, oil and alkaline inhalation, nebulizer therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, UHF and electrophoresis on the chest, microwave therapy, etc. procedures. As a diversionary therapy useful formulation of mustard and cans (cupping massage. When difficulties sputum discharge is assigned to a massage of the chest, vibrating massage, postural drainage, sanation bronchoscopy, physical therapy.
Prevention of Bronchitis in Children
Prevention of bronchitis in children includes the prevention of viral infections, early application of antiviral drugs, elimination of contact with the allergic factors, keeping the child from hypothermia and hardening. The important role played by preventive vaccination of children against influenza and pneumococcal infection.
Children with recurrent and chronic bronchitis require the supervision of a pediatrician and pediatric pulmonologist to persistent cessation of exacerbations in the past 2 years, the anti-relapse treatment in the autumn-winter period. Vaccination is contraindicated in children with allergic bronchitis; the other forms is held in a month after recovery.