Acute Fatty Liver Of Pregnancy
Contents:
An Approach to Diagnosis and Management of Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy (AFLP) is one of the most severe complications during pregnancy. The main thing about it is a high level of death cases. Here the both. A mother and her baby are at risk. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy occurs in one case out of 10000 – 15000 cases of pregnancy. Most often, this illness occurs during the second half of pregnancy (between the 27th and the 40th week). Usually, it occurs on the 36th week of pregnancy.
Risk Factors
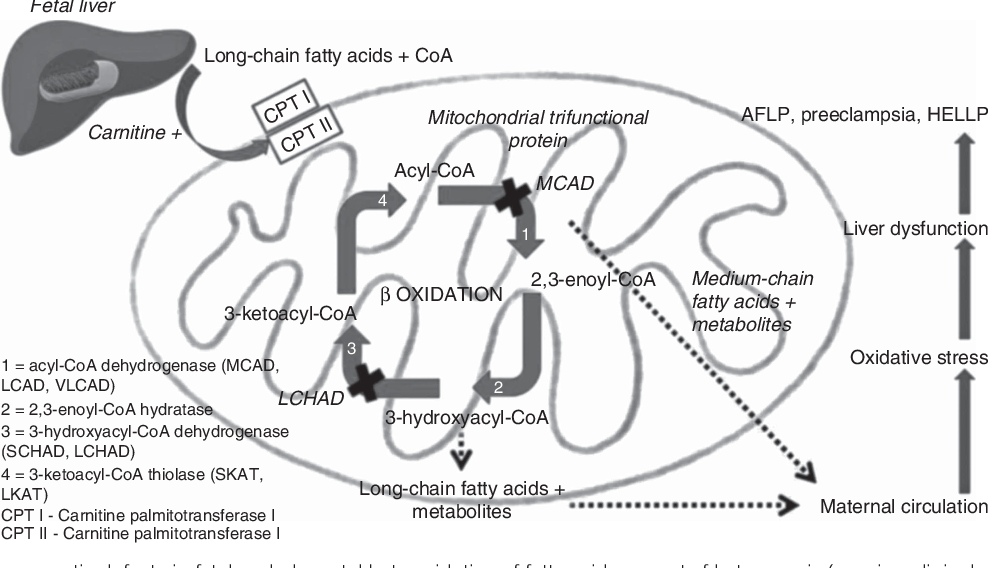
There is no exact geographical or racial inclination to acute fatty liver of pregnancy. The list of the risk factors includes the age of a mother, having a multiple pregnancy, preeclampsia, waiting for a baby boy to be born, a lack of weight and an acute fatty dystrophy in the anamnesis. The studies have shown that women that have (1) a genetic mutation that disturbs mitochondrial acidification of fat acids and a case when (2) a baby doesn’t have 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase chain (LCHAD), are more likely to suffer from this disease.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
Genetic researches of women suffering from acute fatty liver dystrophy, of their husbands and newborn babies have shown that the reason for the development of this and other diseases that are also included in the group of mitochondrial cytopathies (Reye's syndrome, reactions on some drugs, etc.) is gene mutation. This gene is responsible for the occurrence of LCHAD lack. LCHAD is one of four ferments in mitochondrions that are responsible for the splitting of long-chain fat acids.
This pathology of mitochondrions is systematic and it also harms kidneys, muscles, nerve system, pancreas gland, heart. The lack of this ferment leads to the accumulation of fat acids in liver. In the end, it causes the disorder of this function and a possible liver failure. The women that are heterozygous according to the genetic fault, are most likely to suffer from this complication during pregnancy. The researches show that in case of those women that have genetic faults of fat acids acidification the risk of getting ill with acute fatty gestational toxicosis or getting ill with HELLP syndrome is 18 times higher.
However, not all women who have mutation in this gene suffer from this liver pathology. For this reason, there is also a possibility that an acute fatty liver gestational toxicosis may occur during the 3rd trimester as a result of the influence on the organism of a mother. This influence comes from the fetus that also have this genetic fault of fat acids acidification.
Symptoms Acute Fatty Liver in Pregnancy
Usually, symptoms develop during the period of several days to several weeks. They include preicteric period that usually happens on the background of gestational toxicosis. The symptoms include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, weakness, pain in the belly, ascites (as a consequence of portal hypertension), epigastric burning (as an evidence of esophagitis that usually occurs on the background of DIC syndrome) and a developing jaundice. However, there are cases when no jaundice occurs.
Most often, the symptoms occur between the 30th and the 38th week of pregnancy. However, they may occur earlier. You may suffer from transient polyuria and morbid thirst that occur as a result of diabetes insipidus development. The diseases usually is very rough and progresses fast. As a result, it leads to an acute hepatic and kidney failure, development of DIC syndrome and death of a mother and her baby. An acute kidney failure happens in case of 50 % of patients. 60 % have liver encephalopathy that is different due to its transient character and long “easy and light” periods. Approximately 50 % of patients have hypertension, proteinuria and swellings as signs of preeclampsia.
Diagnosing the Disease
Usually, the disease is diagnosed on the basis of a patient’s examination and tests results. In case of the acute fatty liver dystrophy, serum aminotransferase is a bit increased (usually, up to 300-500 UI/l.). The level of bilirubin is not less than 5 mg. /deciliter, however, in very serious cases, it may be even higher. The list of other typical laboratory signs includes leukocytosis (up to 20000 – 30000 in one microliter), thrombocytopenia, hypoproteinemia, and a decrease of prothrombin index (since the protein – synthetic functioning of liver is decreased). There is also hypoglycemia (since there is a disorder of the Krebs cycle). The level of ammonia is increased and neutrophilia occurs. Alkaline phosphatase serum is 5-10 times increased. There is coagulation, metabolic acidosis and signs of kidney failure (oligoanuria, an increase of creatinine and urea).
Visual methods of examination, for example, CT may show diffuse decrease in the thickness of liver and ascites. According to the data of the ultrasonic examination, the liver pathology is usually not evident from the very beginning since fat deposits are microvesicular in their nature. The final diagnosis may be given with the help of liver biopsy. However, this examination is rarely carried out because there is no necessary equipment in the majority of hospitals. Besides, if there is a case of coagulopathy, some complications are likely to occur. The liver biopsy can detect microvesicular steatosis – a case, when drops of fat are located around the central nucleus.
Differential diagnosis includes viral fulminant hepatitis, drug-induced hepatitis, idiopathic cholestasis, Rey’s syndrome, food-borne diseases and other microangiopathies connected with pregnancy: preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
The course of acute viral hepatitis diseases is different on a number of levels: they rarely occur with gestational toxicosis diseases. A developing encephalopathy that with the course of time leads to coma is more likely to occur. Kidney failure occurs rarely. There is an evident increase of ALT from 30 to 100 and higher, there are markers of viral hepatitis diseases in the biochemical blood test (НВsAg, anti-HВcIgM, anti-HDVIgM и IgG, anti-HCV, anti-HAVIgM, anti-HEV and other). Since the tactics of treating an acute viral hepatitis and an acute fatty gestational toxicosis are as different as they can be, it’s of prime importance to exclude viral etiology of the disease. In case of viral hepatitis, the process of labor leads to the course of the hepatitis becoming worse. Therefore, the main aim is keeping the pregnancy safe.
Very often, pregnant women that have nausea and vomiting are diagnosed to have a food-born disease. However, it’s fewer, pains in the lower part of the belly and loose stool that also occur with these diseases. These are never the symptoms of an acute fatty gestational toxicosis. Coffee-grounds vomiting as a sign of DIC syndrome is a characteristic feature of an acute fatty gestational toxicosis.
Differential diagnosis on acute fatty liver dystrophy and HELLP-syndrome is not easy. Especially, when it comes to the partial forms of the syndrome: ELLP syndrome (in case there is no hemolytic anemia). The following things are characteristic features of HEELP syndrome: thrombopenia, erythrocyte hemolysis. Consequently, there is an increase in the level of indirect bilirubin and a significant increase in the level of LDH that is not likely for the acute fatty gestational toxicosis, a low level of haptoglobin serum (less than 1,0 g/l.), this is the most specific and the earliest symptom of intravascular hematolysis. The changes in gemostaziogramma, an increase of alkaline phosphatase level and skin itching are more characteristic symptoms of an acute fatty gestational toxicosis.
Trophopathic hepatitis in case of pregnant women is different since it is better on the part of a mother. Besides, there are increased indexes of cholestasis in blood. The skin itching and steatorrhea are more evident. The same way it happens in case of the acute fatty gestational toxicosis, the changes in coagulation profile occur (blood coagulation time becomes longer). Still, cytological syndrome is less evident.
Treatment Acute Fatty Liver During Pregnancy

Even if there is the slightest suspicion on acute fatty gestational toxicosis in the organism of a pregnant woman, you need to take radical measures and do it very fast since the disease is likely to develop suddenly and very fast. There should be a constant control of the fetus condition and a laboratory control of a mother’s tests. In order to stabilize the condition of a mother it is necessary to inject glucose solutions and have a strict control over the hemodynamics. If there is a necessity, blood products may be used. The most important thing for stopping the development of the disease is the process of labor. It stops the process of liver being overloaded with fat acids. There are also procedures that aim to stabilize the condition of a mother. There is no records on the setback of the acute fatty gestational toxicosis before labor.
The doctors induce the labor in case if the labor through the natural maternal passages is possible and will take, approximately, less than 24 hours. However, according to the researches data, the doctors carry out a procedure of caesarian section in the majority of cases (75 %). This is due to the fact that it can stop the development of the disease faster. Still, there is a need to remember that caesarian section increases the risk of blood transfusion necessity. Obstetricians and anesthesiologists should discuss the method of anesthesia in details.
Some patients may need a general anesthesia because of coagulopathy and an increased risk of hematomas occurring at the places of located anesthesia. In the majority of cases, the condition of a pregnant woman starts improving within 48-72 hours after labor, the level of aminotransferase starts to significantly decrease. However, those women that had signs of coagulopathy, encephalopathy and hypoglycemia when they came to the hospital, are often in need of a constant control and intensive therapy since these patients may sometimes need a transplantation of liver.
Prognosis
Usually, the functioning of liver gets back to normal within a week. However, in some cases, the process of recovery may take several months. Most often, a full recovery occurs. Until recently, the cases of a mother death occurred in 70 % of cases. However, as the methods of diagnosis and intensive therapy have become better and improved, this index decreased up to 7-18 %. As for complications, a bleeding after labor may occur as well as kidney failure, hypoglycemia, pancreatitis and pulmonary edema.
Earlier, the cases of prenatal death also happened more often, in 85 % of cases. According to up-to-date data, it now occurs only in 9-23 % of cases. Since there is a necessity of labor, most babies (75 %) are born prematurely. In average, the gestational age on the time when they are born is 34 weeks. All the babies whose mothers have a case of the acute fatty gestational toxicosis are checked for the genetic faults in the process of fat acids acidification. This way it is possible to detect and start treating them right away. Consequently, the number of death cases and people who get ill with it decrease. The recurrence of the disease in case of the following pregnancies is rare.
However, there are such cases, especially, when it comes to those people who have LCHAD mutation. That’s why there is a need of a strict control over these patients in case they get pregnant again. The control should be carried out by qualified professionals.