Terbutaline in Pregnancy
Contents:
- Terbutaline During Pregnancy
- Effect of the Drug
- Indications for Use
- Intake According to Trimesters of Pregnancy
- Effect on Fetus
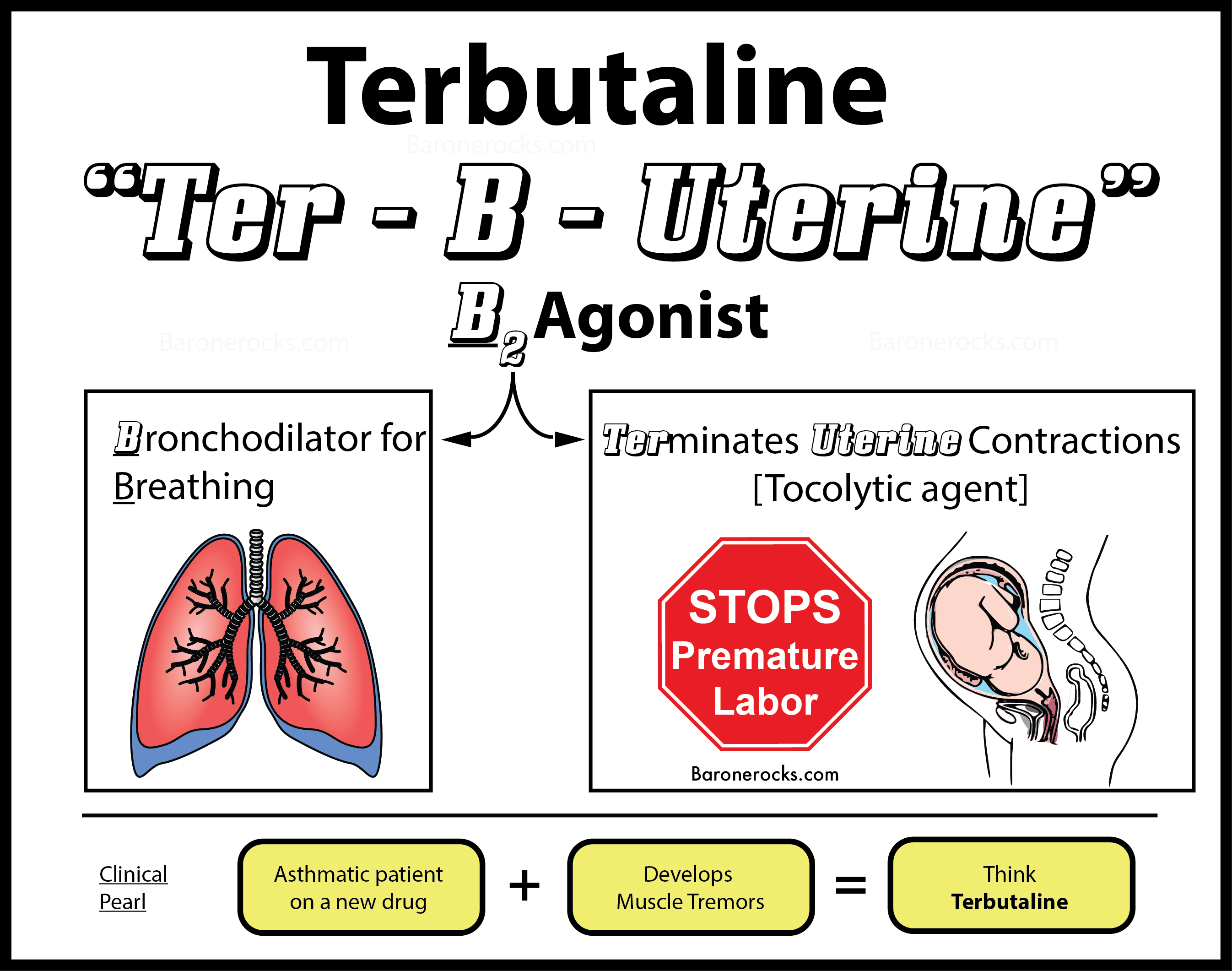
Terbutaline During Pregnancy
Terbutaline is a drug belonging to the group of Adrenergic agonists with tocolytic (relaxes the muscular layer of the uterus), anti-allergic and broncholytic (relaxes smooth muscles of the bronchial tree) effect.
Effect of the Drug
After the intake, the drug is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and binds to beta2-adrenergic receptors, stimulating them.
- In gynecology, this effect leads to a decrease in uterine tone by reducing calcium inside cells; consequently, the uterine muscle relaxes (muscular layer of the uterus), the bloodstream between the placenta and the fetus improves.
- In pulmonology, the drug is used for bronchoectasia and reduction of bronchial mucous viscosity. Terbutaline helps to eliminate pathological substances (bacteria, viruses, dust) and to clear the bronchial tubes.
- The drug inhibits the release of mediators of allergic reactions (histamine, serotonin), stabilizes cell membranes and prevents accumulation of extra interstitial fluid (edema) that helps to eliminate allergies.
Indications for Use
- primary dysmenorrhea (disorders in menstrual cycle);
- the threat of premature birth;
- threatening abortion (from the 16th week of pregnancy);
- suturing on the cervix to fix its premature opening;
- the threat of development of uterine rupture in case of too intense contractions and incomplete opening of the cervix;
- preparation of a pregnant woman to cesarean section;
- bronchial asthma;
- status asthmaticus;
- pulmonary emphysema;
- intractable especially acute bronchitis;
- acute heart failure;
- Quincke's disease;
- angioneurotic edema;
- allergic reactions on the skin.
Intake According to Trimesters of Pregnancy
In obstetric practice, Terbutaline is prescribed in the first and the second trimesters of pregnancy to prevent miscarriage. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the drug is prescribed in the form of tablets or solution for injections under the threat of development of premature delivery, and in the presence of a vibrant labor, accompanied by the threat of uterine rupture development.
Tablets are ingested in fasting state washing down with clean, cool water for 5 mg (2 tablets) every 6 hours. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 15 mg.
The injection is made subcutaneously into the lateral (side) surface of the deltoid muscle in a dose of 0,25 mg; if the effect through 20-30 minutes after the injection does not come, the re-injection in a dose of 0,25 mg is produced. The next introduction of the drug is in no event sooner than 4-5 hours.
As a bronchodilator, Terbutaline can be assigned only in the third trimester on strict medical indications, when the risk to the mother's health will be higher than the risk of the drug intake to the fetus in the form of aerosols for inhalation or subcutaneous injection.
The aerosol for inhalation is prescribed as 2 inhalations up to 4-5 times per day.
The Injection is made subcutaneously in the lateral surface of the deltoid muscle in a dosage of 0.25 mg every 4-5 hours.
Effect on Fetus
The intake of Terbutaline may produce the following effects on fetal development:
- increase in arterial blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- blood sugar level reduction;
- pulmonary edema.
Intake During Lactation
It is necessary to abandon breastfeeding and replace it with infant formula milk during the period of Terbutaline intake.