Premature Babies

Contents:
- When is a Baby Considered Premature
- Classification of Premature Babies
- The Reasons for Why Babies are Born Earlier than Necessary
- Symptoms of a Premature Baby
- Therapy in Case of Premature Babies
- Feeding Premature Babies at Home
- Consequences in Case of Premature Babies and Prognosis
When is a Baby Considered Premature
A premature baby is a baby that’s born before the end of the gestational period, somewhere between the 22nd and the 37th week. A premature baby weighs less than 2500 g and his/her height is less than 45 cm. Premature babies suffer from thermoregulation disorder and inspiratory apnea (no breathing for some time). They have weak immune system and obvious clinical and anthropometric signs.
Classification of Premature Babies
The classification is based on the weight of a baby (the term of pregnancy when he/she was born is not that important):
- The 1st group – premature babies that weigh 2001-2500 g. (approximately the 35-37th week);
- The 2nd group – premature babies that weigh 1501-2000 g. (approximately the 32-34th week);
- The 3rd group – premature babies that weigh 1100-1500 g. (approximately the 29-31st week);
- The 4th group – premature babies that weigh less than 1000 g. The gestational term is less than 29 weeks. (Babies that refer to this group are considered to be extremely premature).
The Reasons for Why Babies are Born Earlier than Necessary
There are different reasons for advanced labour. In overall, there exist 3 groups of these reasons (factors).
Factors on the part of a mother:
- chronic diseases (pathologies of the cardio-vascular system, diseases of the endocrine system, pathologies of the kidneys);
- acute infections that occur during the period of pregnancy;
- gynecological diseases;
- serious negative factors mentioned in the obstetric history (cases of caesarean section and abortion);
- intrauterine device;
- traumas;
- cervical insufficiency;
- age (a woman is under 17 or over 30);
- Rh-incompatible pregnancy;
- bad health habits;
- placenta pathologies (presentation, abruption of placenta);
- harmful work environment;
- complications that occur during pregnancy (gestosis).
Factors on the part of a father:
- a father is over 50;
- chronic diseases.
Pregnancy factors:
- prenatal pathologies in the development of a baby;
- multiple pregnancy;
- erythroblastosis (hematolytic disease);
- prenatal infection.
Symptoms of a Premature Baby
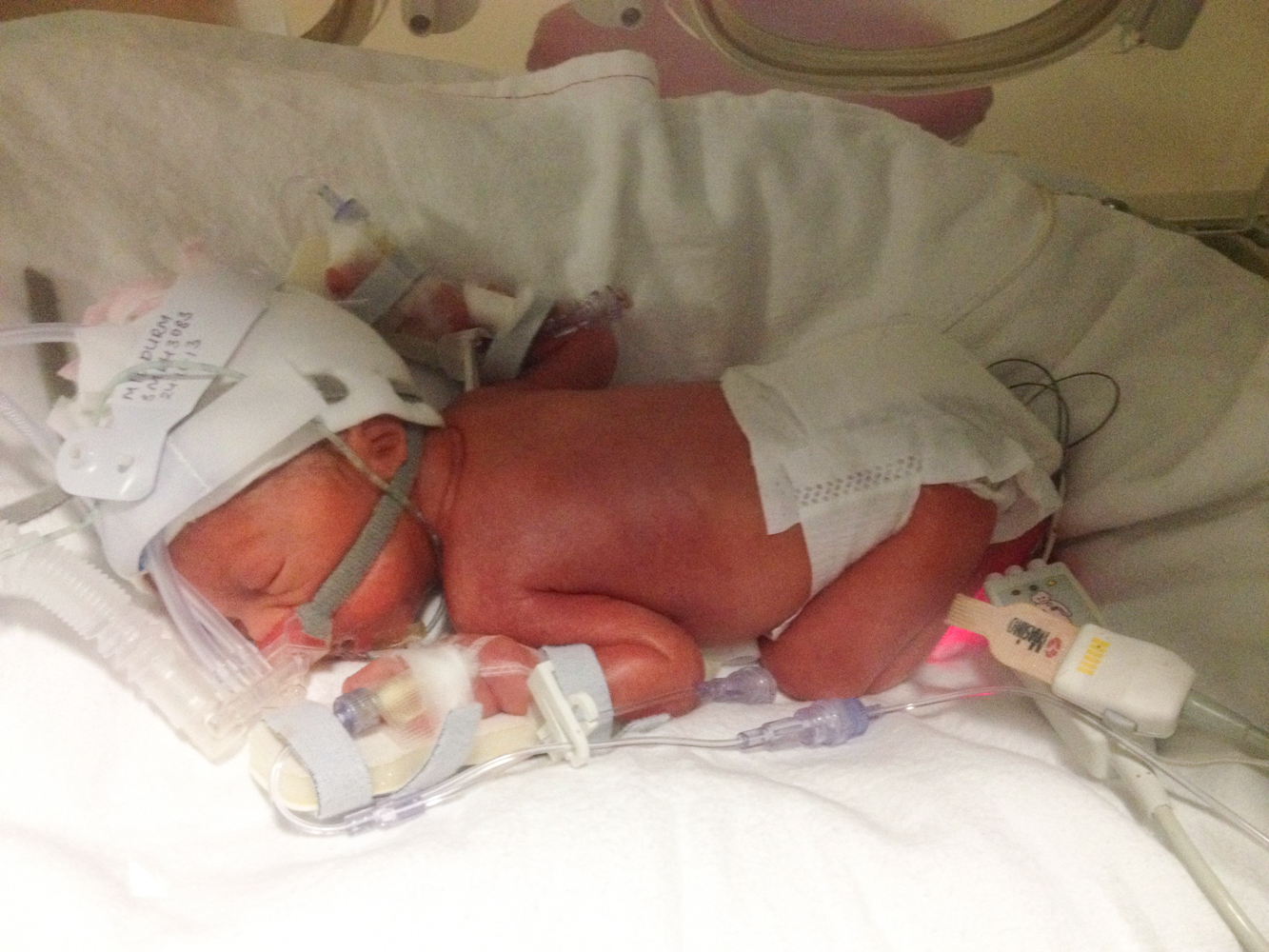
Premature babies have obvious clinical symptoms. There is the disproportion of body parts, the head (the skull) is bigger than the facial area. The bones of the skull are soft. Even though there are fontanels, there is the non-closure of the cranial structures. Besides, the earflaps are soft.
The subcutaneous tissue of the premature babies is not that good. That’s why they can’t “keep” temperature (thermoregulation is unstable). Premature babies suffer from pulmonary hypoplasia because there is no surfactant that allows the bronchic cells to open when a baby breathes in. That’s why there is a respiratory system disorder. Sometimes, apnea occurs (stop of breathing).
The skin integument is rugate. During the first 24 hours, the skin integument is bright red in color. The muscle tone is weak. Actually, there may be no muscle tone at all. Physiologic reflexes (sucking reflex, search reflex etc.) are quite weak.
In case of premature boys, testes are not in the marsupium. Premature girls have underdeveloped outer labia. Premature kids have syndrome of hydrocephalus and hypertensive syndrome. Due to the fact that eyelids are underdeveloped, premature babies have google eyes (exophthalmos).
Since the liver of premature babies doesn’t function the way it should, there occurs kemicterus. Since the immune system of premature babies is quite weak, they are very prone to getting infected. Premature babies regurgate very often. Besides, such like babies have underdeveloped nail plates. They can cover only the half of the area.
Therapy in Case of Premature Babies
Neonatologist is a doctor who treats premature babies. If a baby is born earlier than necessary, he/she needs special environment. The temperature should be 25 °C and the air humidity should be not less than 55-60 %. That’s why premature babies are to be in a couveuse (special incubation apparatus).
Those babies who weigh less than 2000 g. are to be kept in couveuses. Premature babies are discharged from the hospital on the 8-10th day after they were born under the condition that they weigh 2000 g. when discharged.
In case a premature baby’s weight doesn’t reach 2000 g. within 14 days, such a baby is provided additional nursing therapy. Such a baby is kept in a couveuse in ET room of the babies’ department or a hospital. A baby is lying in a couveuse to which a special equipment providing him/her with oxygen is connected.
Premature babies are allowed to take a bath starting from the time they turn 2 weeks old, under the condition that umbilical cord remnant has healed. When such like babies turn 3-4 weeks old and weigh 1700-1800 g., it’s allowed to take them for a walk. Premature babies are discharged from a hospital once their weight reaches 1700 g.
Feeding Premature Babies at Home

A baby is fed with expressed milk 2-6 after he/she was born under the condition that there are no contradictions and the term of pregnancy was somewhere between 34-37 weeks.
If it’s about extremely premature babies and a babies that are in critical condition, such like babies are provided with feeding with the help of an enteral feeding tube (to the mouth/nose). This is the way babies are fed during the first 24-48 hours of their lives.
If a baby can actively suck, he/she may be breastfed under the condition that he/she weighs 1800-2000 g. On the 1st day, the amount of the feeding necessary is 5-10 ml. On the 2nd day 10-15 ml. On the 3rd day 15-20 ml.
Besides, premature babies should be provided with a number of vitamins (enlisted below):
- Vicasol (vitamin K) in order to prevent intracraneal hemorrhage;
- Cevitamic acid (vitamin C), vitamins B1 and B2;
- Vitamin E (Tocopherol);
- Vitamin D – a preventive measure against rickets;
- Vitamins B6 and B5, lipoic acid (in cases a baby is extremely premature).
Consequences in Case of Premature Babies and Prognosis
Prognosis in terms of future development of premature babies depends on a number of factors. The first factor is the term of pregnancy when such a baby was born and his/her weigh. In case a baby is born on the 22-23rd week, the prognosis depends on the intensity and quality of the therapy provided.
There is an increased risk of fatal outcome under the following conditions:
- pre-delivery bleeding;
- breech presentation;
- multiple pregnancy;
- asphyxia of the baby (during labour);
- low body temperature of a baby;
- respiratory distress syndrome.
There may be other consequences in case a baby is premature. The risk of their occurrence also depends on a number of factors.
If the condition of a baby is fine in overall, these consequences are not likely to occur):
- Developmental cognitive and physical multiplication;
- Infantile cerebral paralysis;
- Сonvulsive disorder and syndrome of hydrocephalus;
- Myopia, astigmatism, glaucoma and retinal detachment;
- A baby is very prone to getting infections;
- Hearing disorder;
- Menstrual disorder and sex infantilism, it may be hard for girls to get pregnant.