Nipt Test
Contents:
- Non Invasive Prenatal Testing
- When NIPT is Recommended
- When NIPT is Done?
- How a Fetal Genetic Abnormality Screening is Performed?
Non Invasive Prenatal Testing
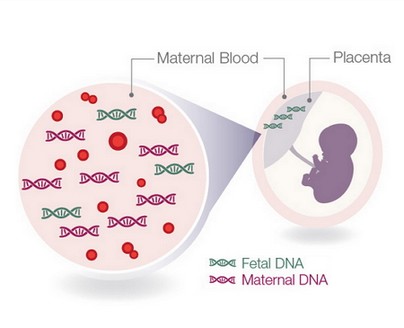
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a method of testing the fetus’s DNA in the blood of the mother to see if it’s affected by any of the most common chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, Turner syndrome), and to detect the baby’s gender.
Until recently there was no screening test for microdeletion syndrome and other genetic abnormalities caused by missing or additional chromosomal parts.
An ultrasound scan doesn’t give an accurate result, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. An invasive test that has a minor risk of miscarriage is the only way to get an accurate result. Panorama is a safe and accurate non-invasive prenatal test that screens for microdeletion.
During pregnancy, a small amount of the fetal DNA circulates in the mother’s blood flow. This DNA contains genetic information about the baby and its chromosomes. Screening this DNA allows to detect certain abnormalities that can affect the baby’s health.
Non-invasive prenatal DNA test:
- Safe for the mother and baby: no invasive procedures, no hospital admission, no preparation;
- 10 ml of a mother’s venous blood is enough for the test (not an amniotic fluid as in amneocentesis or fetal blood as in cordocentesis);
- High accuracy;
- Can be performed as early as the 9th week of pregnancy.
When NIPT is Recommended
- If chromosomal abnormality is suspected after an ultrasound scan;
- If a biochemical testing in the first and/or second trimester showed an aneuploidy risk;
- Previous miscarriages;
- Familial genetic diseases or children with chromosomal abnormalities;
- Infertility;
- Previous stillbirths or children with developmental anomalies;
- Using in vitro fertilization;
- If the pregnant woman is 35 or older.
It’s known that aneuploidy can’t be detected any other way during pregnancy, so NIPT is really recommended to all women who want to be sure that their future baby is healthy.
When NIPT is Done?
NIPT can be done not earlier than the 9th week of the pregnancy. At the earlier stages the amount of fetal DNA in the mother’s blood can be insufficient for the test.
After the 9th week of pregnancy, NIPT can be performed at any stage. However, don’t forget that after the 25th week of pregnancy you won’t have enough time to take an additional test if a risk detected (for example, an amniocentesis).
How a Fetal Genetic Abnormality Screening is Performed?
A doctor can recommend non-invasive prenatal test or a woman can decide to take it herself.
A doctor takes venous blood for the test. It is performed regardless of the eating time, but it’s recommended to eat something sweet (like, a chocolate bar or a juice) 20 minutes before the test. That will help to increase the amount of fetal DNA in your blood.
A woman needs to see a gynecologist before the test to confirm that she is past the 9th week of her pregnancy. Also, the gynecologist gives the referral for the test. The woman needs to take a recent ultrasound scan result to the test (taken no longer than 1 week ago).
If a high risk of chromosomal abnormality is detected, the woman will be recommended to see a genetics counselor who will explain the findings of the test and help to make the right decision.